A casein kinase 1 and PAR proteins regulate asymmetry of a PIP(2) synthesis enzyme for asymmetric spindle positioning
- PMID: 18694560
- PMCID: PMC2686839
- DOI: 10.1016/j.devcel.2008.06.002
A casein kinase 1 and PAR proteins regulate asymmetry of a PIP(2) synthesis enzyme for asymmetric spindle positioning
Abstract
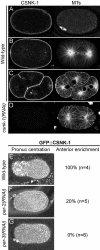
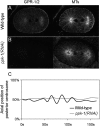
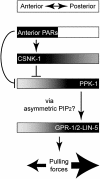
Spindle positioning is an essential feature of asymmetric cell division. The conserved PAR proteins together with heterotrimeric G proteins control spindle positioning in animal cells, but how these are linked is not known. In C. elegans, PAR protein activity leads to asymmetric spindle placement through cortical asymmetry of Galpha regulators GPR-1/2. Here, we establish that the casein kinase 1 gamma CSNK-1 and a PIP(2) synthesis enzyme (PPK-1) transduce PAR polarity to asymmetric Galpha regulation. PPK-1 is posteriorly enriched in the one-celled embryo through PAR and CSNK-1 activities. Loss of CSNK-1 causes uniformly high PPK-1 levels, high symmetric cortical levels of GPR-1/2 and LIN-5, and increased spindle pulling forces. In contrast, knockdown of ppk-1 leads to low GPR-1/2 levels and decreased spindle forces. Furthermore, loss of CSNK-1 leads to increased levels of PIP(2). We propose that asymmetric generation of PIP(2) by PPK-1 directs the posterior enrichment of GPR-1/2 and LIN-5, leading to posterior spindle displacement.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Asymmetrically distributed C. elegans homologs of AGS3/PINS control spindle position in the early embryo.Curr Biol. 2003 Jun 17;13(12):1029-37. doi: 10.1016/s0960-9822(03)00371-3. Curr Biol. 2003. PMID: 12814548
-
LET-99 opposes Galpha/GPR signaling to generate asymmetry for spindle positioning in response to PAR and MES-1/SRC-1 signaling.Development. 2003 Dec;130(23):5717-30. doi: 10.1242/dev.00790. Epub 2003 Oct 8. Development. 2003. PMID: 14534135
-
Dynamic localization of LIN-5 and GPR-1/2 to cortical force generation domains during spindle positioning.Dev Biol. 2008 Mar 1;315(1):42-54. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2007.11.037. Epub 2007 Dec 14. Dev Biol. 2008. PMID: 18234174 Free PMC article.
-
Polarity establishment, asymmetric division and segregation of fate determinants in early C. elegans embryos.WormBook. 2014 Dec 30:1-43. doi: 10.1895/wormbook.1.30.2. WormBook. 2014. PMID: 25548889 Review.
-
Spindle positioning during the asymmetric first cell division of Caenorhabditis elegans embryos.Novartis Found Symp. 2001;237:164-75; discussion 176-81. doi: 10.1002/0470846666.ch13. Novartis Found Symp. 2001. PMID: 11444042 Review.
Cited by
-
The coordination of spindle-positioning forces during the asymmetric division of the Caenorhabditis elegans zygote.EMBO Rep. 2021 May 5;22(5):e50770. doi: 10.15252/embr.202050770. Epub 2021 Apr 26. EMBO Rep. 2021. PMID: 33900015 Free PMC article.
-
Multiple Aspects of PIP2 Involvement in C. elegans Gametogenesis.Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Sep 10;19(9):2679. doi: 10.3390/ijms19092679. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 30201859 Free PMC article.
-
Intracellular organelles mediate cytoplasmic pulling force for centrosome centration in the Caenorhabditis elegans early embryo.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011 Jan 4;108(1):137-42. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1013275108. Epub 2010 Dec 20. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011. PMID: 21173218 Free PMC article.
-
NuMA interacts with phosphoinositides and links the mitotic spindle with the plasma membrane.EMBO J. 2014 Aug 18;33(16):1815-30. doi: 10.15252/embj.201488147. Epub 2014 Jul 4. EMBO J. 2014. PMID: 24996901 Free PMC article.
-
FAM83D directs protein kinase CK1α to the mitotic spindle for proper spindle positioning.EMBO Rep. 2019 Sep;20(9):e47495. doi: 10.15252/embr.201847495. Epub 2019 Jul 24. EMBO Rep. 2019. PMID: 31338967 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Afshar K., Willard F.S., Colombo K., Siderovski D.P., Gonczy P. Cortical localization of the Gα protein GPA-16 requires RIC-8 function during C. elegans asymmetric cell division. Development. 2005;132:4449–4459. - PubMed
-
- Betschinger J., Knoblich J.A. Dare to be different: asymmetric cell division in Drosophila, C. elegans and vertebrates. Curr. Biol. 2004;14:R674–R685. - PubMed
-
- Bowman S.K., Neumuller R.A., Novatchkova M., Du Q., Knoblich J.A. The Drosophila NuMA homolog Mud regulates spindle orientation in asymmetric cell division. Dev. Cell. 2006;10:731–742. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

