Small ubiquitin-related modifier (SUMO)-1, SUMO-2/3 and SUMOylation are involved with centromeric heterochromatin of chromosomes 9 and 1 and proteins of the synaptonemal complex during meiosis in men
- PMID: 18694876
- PMCID: PMC2583944
- DOI: 10.1093/humrep/den300
Small ubiquitin-related modifier (SUMO)-1, SUMO-2/3 and SUMOylation are involved with centromeric heterochromatin of chromosomes 9 and 1 and proteins of the synaptonemal complex during meiosis in men
Abstract
Background: Post-transcriptional modification by SUMOylation is involved in numerous cellular processes including human spermatogenesis. For human male meiosis, we previously showed that the small ubiquitin-related modifier-1 (SUMO-1) protein localizes to chromatin axes in early pachytene spermatocytes, then to kinetochores as meiosis progresses. Here, we delineate possible functional roles based on subcellular localization for SUMO-1 and SUMO-2/3.
Methods: Western and immunoprecipitation analyses were conducted on proteins isolated from the testis of two normal adult fertile men. Combinatorial immunofluorescence and chromosome-specific fluorescence in situ hybridization analyses were performed on male meiocytes obtained during testicular biopsy from four patients undergoing testicular sperm extraction for assisted reproduction technologies.
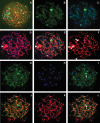
Results: The synaptonemal complex (SC) and SC proteins (SCP)-1 and SCP2, but not SCP3, are SUMOylated by SUMO-1 during the pachytene substage. Likewise, two distinct localization patterns for SUMO-1 are identified: a linear pattern co-localized with autosomal SCs and isolated SUMO-1 near the centromeric heterochromatin of chromosomes 9 and 1. In contrast to SUMO-1, which is not detectable prior to pachytene in normal tissue, SUMO-2/3 is identified as early as leptotene and zygotene and in some, but not all, pachytene cells; no linear patterns were detected. Similar to SUMO-1, SUMO-2/3 localizes in two predominant subnuclear patterns: a single, dense signal near the centromere of human chromosome 9 and small, individual foci co-localized with autosomal centromeres.
Conclusions: Our data suggest that SUMO-1 may be involved in maintenance and/or protection of the autosomal SC. SUMO-2/3, though expressed similarly, may function separately and independently during pachytene in men.
Figures


Similar articles
-
SUMO-1, human male germ cell development, and the androgen receptor in the testis of men with normal and abnormal spermatogenesis.Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2006 May;290(5):E1022-33. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.00527.2005. Epub 2005 Dec 13. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2006. PMID: 16352666
-
Chronology of meiosis & synaptonemal complex abnormalities in normal & abnormal spermatogenesis.Indian J Med Res. 2009 Mar;129(3):268-78. Indian J Med Res. 2009. PMID: 19491419
-
SUMO meets meiosis: an encounter at the synaptonemal complex: SUMO chains and sumoylated proteins suggest that heterogeneous and complex interactions lie at the centre of the synaptonemal complex.Bioessays. 2011 Jul;33(7):529-37. doi: 10.1002/bies.201100002. Epub 2011 May 17. Bioessays. 2011. PMID: 21590786 Review.
-
Testicular expression of small ubiquitin-related modifier-1 (SUMO-1) supports multiple roles in spermatogenesis: silencing of sex chromosomes in spermatocytes, spermatid microtubule nucleation, and nuclear reshaping.Dev Biol. 2005 Jun 15;282(2):480-92. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2005.03.034. Dev Biol. 2005. PMID: 15950612
-
Wrestling with Chromosomes: The Roles of SUMO During Meiosis.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2017;963:185-196. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-50044-7_11. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2017. PMID: 28197913 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Temporal and SUMO-specific SUMOylation contribute to the dynamics of Polo-like kinase 1 (PLK1) and spindle integrity during mouse oocyte meiosis.Dev Biol. 2018 Feb 15;434(2):278-291. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2017.12.011. Epub 2017 Dec 19. Dev Biol. 2018. PMID: 29269218 Free PMC article.
-
SUMOylation-Mediated Regulation of Cell Cycle Progression and Cancer.Trends Biochem Sci. 2015 Dec;40(12):779-793. doi: 10.1016/j.tibs.2015.09.006. Epub 2015 Oct 22. Trends Biochem Sci. 2015. PMID: 26601932 Free PMC article. Review.
-
SENP3 grants tight junction integrity and cytoskeleton architecture in mouse Sertoli cells.Oncotarget. 2017 Apr 7;8(35):58430-58442. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.16915. eCollection 2017 Aug 29. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 28938568 Free PMC article.
-
Structural analysis of the human SYCE2-TEX12 complex provides molecular insights into synaptonemal complex assembly.Open Biol. 2012 Jul;2(7):120099. doi: 10.1098/rsob.120099. Open Biol. 2012. PMID: 22870393 Free PMC article.
-
Focal Adhesion Protein Vinculin Is Required for Proper Meiotic Progression during Mouse Spermatogenesis.Cells. 2022 Jun 23;11(13):2013. doi: 10.3390/cells11132013. Cells. 2022. PMID: 35805097 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Antonelli A, Gandini L, Petrinelli P, Marcucci L, Elli R, Lombardo F, Dondero F, Lenzi A. Chromosomal alterations and male infertility. J Endocrinol Invest. 2000;23:677–683. - PubMed
-
- Azuma Y, Tan SH, Cavenagh MM, Ainsztein AM, Saitoh H, Dasso M. Expression and regulation of the mammalian SUMO-1 E1 enzyme. FASEB J. 2001;15:1825–1827. - PubMed
-
- Barlow AL, Hultén MA. Combined immunocytogenetic and molecular cytogenetic analysis of meiosis I human spermatocytes. Chromosome Res. 1996;4:562–573. - PubMed

