Control over the contribution of the mitochondrial membrane potential (DeltaPsi) and proton gradient (DeltapH) to the protonmotive force (Deltap). In silico studies
- PMID: 18694940
- PMCID: PMC2662253
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M802404200
Control over the contribution of the mitochondrial membrane potential (DeltaPsi) and proton gradient (DeltapH) to the protonmotive force (Deltap). In silico studies
Abstract
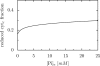
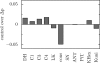
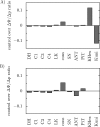
The protonmotive force across the inner mitochondrial membrane (Deltap) has two components: membrane potential (DeltaPsi) and the gradient of proton concentration (DeltapH). The computer model of oxidative phosphorylation developed previously by Korzeniewski et al. (Korzeniewski, B., Noma, A., and Matsuoka, S. (2005) Biophys. Chem. 116, 145-157) was modified by including the K+ uniport, K+/H+ exchange across the inner mitochondrial membrane, and membrane capacitance to replace the fixed DeltaPsi/DeltapH ratio used previously with a variable one determined mechanistically. The extended model gave good agreement with experimental results. Computer simulations showed that the contribution of DeltaPsi and DeltapH to Deltap is determined by the ratio of the rate constants of the K+ uniport and K+/H+ exchange and not by the absolute values of these constants. The value of Deltap is mostly controlled by ATP usage. The metabolic control over the DeltaPsi/DeltapH ratio is exerted mostly by K+ uniport and K+/H+ exchange in the presence of these processes, and by the ATP usage, ATP/ADP carrier, and phosphate carrier in the absence of them. The K+ circulation across the inner mitochondrial membrane is controlled mainly by K+ uniport and K+/H+ exchange, whereas H+ circulation by ATP usage. It is demonstrated that the secondary K+ ion transport is not necessary for maintaining the physiological DeltaPsi/DeltapH ratio.
Figures
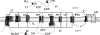


References
-
- Mitchell P. (1961) Nature 191 144-148 - PubMed
-
- Duszyński, J., Bogucka, K., and Wojtczak, L. (1984) Biochim. Biophys. Acta 767 540-547 - PubMed
-
- Kunz, W., Gellerich, F. N., Schild, L., and Schönfeld, P. (1988) FEBS Lett. 233 17-21 - PubMed
-
- Ouhabi, R., Rigoulet, M., Lavie, J.-L., and Guérin, B. (1991) Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1060 293-298 - PubMed
-
- Czyż, A., Szewczyk, A., Nałęcz, J., and Wojtczak, L. (1995) Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 210 98-104 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

