Role of protein kinase A in Trypanosoma cruzi
- PMID: 18694966
- PMCID: PMC2546855
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.00527-08
Role of protein kinase A in Trypanosoma cruzi
Abstract
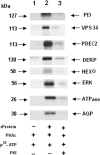
Protein kinase A (PKA) is an important mediator of many signal transduction pathways that occur in eukaryotic cells, and it has been implicated as a regulator of stage differentiation in Trypanosoma cruzi. To evaluate the importance of the PKA catalytic subunit of T. cruzi (TcPKAc), a gene encoding a PKA inhibitor (PKI) containing a specific PKA pseudosubstrate, R-R-N-A, was subcloned into a pTREX vector and introduced into epimastigotes by electroporation. Expression of PKI has a lethal effect in this parasite. Similarly, a pharmacological inhibitor, H89, killed epimastigotes at a concentration of 10 muM. To understand the biology of PKA, identification of the particular substrates of this enzyme is essential. Using a yeast two-hybrid system, 38 candidates interacting with TcPKAc were identified. Eighteen of these were hypothetical proteins with unknown functions, while the others had putative or known functions. The entire open reading frames of eight genes presumably important in regulating T. cruzi growth, adaptation, and differentiation, including a type III PI3 kinase (Vps34), a putative PI3 kinase, a putative mitogen-activated extracellular signal-regulated kinase, a cyclic AMP (cAMP)-specific phosphodiesterase (PDEC2), a hexokinase, a putative ATPase, a DNA excision repair protein, and an aquaporin were confirmed to interact with TcPKAc in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae under the highest stringency selection conditions, and PKA phosphorylated the recombinant proteins of these genes. Taken together, these findings demonstrate the importance of cAMP-PKA signaling in this organism.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Protein kinase A catalytic subunit interacts and phosphorylates members of trans-sialidase super-family in Trypanosoma cruzi.Microbes Infect. 2010 Sep;12(10):716-26. doi: 10.1016/j.micinf.2010.04.014. Epub 2010 May 11. Microbes Infect. 2010. PMID: 20466066 Free PMC article.
-
Protein kinase A regulatory subunit interacts with P-Type ATPases in Trypanosoma cruzi.Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2009 Jun;80(6):941-3. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2009. PMID: 19478254
-
Molecular cloning and expression of the catalytic subunit of protein kinase A from Trypanosoma cruzi.Int J Parasitol. 2002 Aug;32(9):1107-15. doi: 10.1016/s0020-7519(02)00085-1. Int J Parasitol. 2002. PMID: 12117493
-
Signal transduction in Trypanosoma cruzi.Adv Parasitol. 2011;75:325-44. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-385863-4.00015-0. Adv Parasitol. 2011. PMID: 21820563 Review.
-
Exploring the Plasmodium falciparum cyclic-adenosine monophosphate (cAMP)-dependent protein kinase (PfPKA) as a therapeutic target.Microbes Infect. 2012 Aug;14(10):838-50. doi: 10.1016/j.micinf.2012.05.004. Epub 2012 May 22. Microbes Infect. 2012. PMID: 22626931 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Large-Scale Phylogenetic Analysis of Trypanosomatid Adenylate Cyclases Reveals Associations with Extracellular Lifestyle and Host-Pathogen Interplay.Genome Biol Evol. 2020 Dec 6;12(12):2403-2416. doi: 10.1093/gbe/evaa226. Genome Biol Evol. 2020. PMID: 33104188 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular cloning and characterization of mitogen-activated protein kinase 2 in Trypanosoma cruzi.Cell Cycle. 2010 Jul 15;9(14):2888-96. doi: 10.4161/cc.9.14.12372. Epub 2010 Jul 13. Cell Cycle. 2010. PMID: 20603604 Free PMC article.
-
Reprogramming of Trypanosoma cruzi metabolism triggered by parasite interaction with the host cell extracellular matrix.PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2019 Feb 6;13(2):e0007103. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0007103. eCollection 2019 Feb. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2019. PMID: 30726203 Free PMC article.
-
Trypanosoma cruzi DNA Polymerase β Is Phosphorylated In Vivo and In Vitro by Protein Kinase C (PKC) and Casein Kinase 2 (CK2).Cells. 2022 Nov 21;11(22):3693. doi: 10.3390/cells11223693. Cells. 2022. PMID: 36429121 Free PMC article.
-
cAMP signalling in trypanosomatids: role in pathogenesis and as a drug target.Trends Parasitol. 2015 Aug;31(8):373-9. doi: 10.1016/j.pt.2015.04.014. Epub 2015 May 21. Trends Parasitol. 2015. PMID: 26004537 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Alonso, G. D., A. C. Schoijet, H. N. Torres, and M. M. Flawiá. 2007. TcrPDEA1, a cAMP-specific phosphodiesterase with atypical pharmacological properties from Trypanosoma cruzi. Mol. Biochem. Parasitol. 15272-79. - PubMed
-
- Broach, J. R. 1991. RAS genes in Saccharomyces cerevisiae: signal transduction in search of a pathway. Trends Genet. 728-33. - PubMed
-
- Cáceres, A. J., W. Quiñones, M. Gualdrón, A. Cordeiro, L. Avilán, P. A. Michels, and J. L. Concepción. 2007. Molecular and biochemical characterization of novel glucokinases from Trypanosoma cruzi and Leishmania spp. Mol. Biochem. Parasitol. 156235-245. - PubMed
-
- Chijiwa, T., A. Mishima, M. Hagiwara, M. Sano, K. Hayashi, T. Inoue, K. Naito, T. Toshioka, and H. Hidaka. 1990. Inhibition of forskolin-induced neurite outgrowth and protein phosphorylation by a newly synthesized selective inhibitor of cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase, N-[2-(p-bromocinnamylamino)ethyl]-5-isoquinolinesulfonamide (H-89), of PC12D pheochromocytoma cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2655267-5272. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

