Red cell life span heterogeneity in hematologically normal people is sufficient to alter HbA1c
- PMID: 18694998
- PMCID: PMC2581997
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2008-04-154112
Red cell life span heterogeneity in hematologically normal people is sufficient to alter HbA1c
Abstract
Although red blood cell (RBC) life span is a known determinant of percentage hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c), its variation has been considered insufficient to affect clinical decisions in hematologically normal persons. However, an unexplained discordance between HbA1c and other measures of glycemic control can be observed that could be, in part, the result of differences in RBC life span. To explore the hypothesis that variation in RBC life span could alter measured HbA1c sufficiently to explain some of this discordance, we determined RBC life span using a biotin label in 6 people with diabetes and 6 nondiabetic controls. Mean RBC age was calculated from the RBC survival curve for all circulating RBCs and for labeled RBCs at multiple time points as they aged. In addition, HbA1c in magnetically isolated labeled RBCs and in isolated transferrin receptor-positivereticulocytes was used to determine the in vivo synthetic rate of HbA1c. The mean age of circulating RBCs ranged from 39 to 56 days in diabetic subjects and 38 to 60 days in nondiabetic controls. HbA1c synthesis was linear and correlated with mean whole blood HbA1c (R(2) = 0.91). The observed variation in RBC survival was large enough to cause clinically important differences in HbA1c for a given mean blood glucose.
Figures
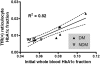
 ), 95% confidence intervals.
), 95% confidence intervals.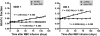
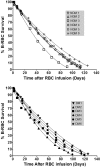
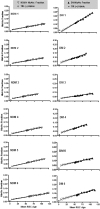
 ), 95% confidence intervals.
), 95% confidence intervals.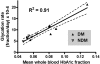

References
-
- Higgins PJ, Bunn HF. Kinetic analysis of the nonenzymatic glycosylation of hemoglobin. J Biol Chem. 1981;256:5204–5208. - PubMed
-
- Svendsen PA, Christiansen JS, Soegaard U, Nerup J. Synthesis of glycosylated haemoglobin in vivo. Diabetologia. 1981;21:549–553. - PubMed
-
- Rohlfing C, Wiedmeyer HM, Little R, et al. Biological variation of glycohemoglobin. Clin Chem. 2002;48:1116–1118. - PubMed
-
- Nathan DM, Singer DE, Hurxthal K, Goodson JD. The clinical information value of the glycosylated hemoglobin assay. N Engl J Med. 1984;310:341–346. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

