T cell-independent development and induction of somatic hypermutation in human IgM+ IgD+ CD27+ B cells
- PMID: 18695003
- PMCID: PMC2526198
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.20070447
T cell-independent development and induction of somatic hypermutation in human IgM+ IgD+ CD27+ B cells
Abstract
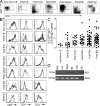
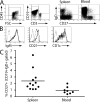
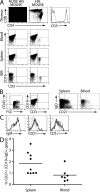
IgM(+)IgD(+)CD27(+) B cells from peripheral blood have been described as circulating marginal zone B cells. It is still unknown when and where these cells develop. These IgM(+)IgD(+)CD27(+) B cells exhibit somatic hypermutations (SHMs) in their B cell receptors, but the exact nature of the signals leading to induction of these SHMs remains elusive. Here, we show that IgM(+)IgD(+)CD27(+) B cells carrying SHMs are observed during human fetal development. To examine the role of T cells in human IgM(+)IgD(+)CD27(+) B cell development we used an in vivo model in which Rag2(-/-)gamma(C)(-/-) mice were repopulated with human hematopoietic stem cells. Using Rag2(-/-)gamma(C)(-/-) mice on a Nude background, we demonstrated that development and induction of SHMs of human IgM(+)IgD(+)CD27(+) B cells can occur in a T cell-independent manner.
Figures
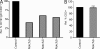
Similar articles
-
Human immunoglobulin (Ig)M+IgD+ peripheral blood B cells expressing the CD27 cell surface antigen carry somatically mutated variable region genes: CD27 as a general marker for somatically mutated (memory) B cells.J Exp Med. 1998 Nov 2;188(9):1679-89. doi: 10.1084/jem.188.9.1679. J Exp Med. 1998. PMID: 9802980 Free PMC article.
-
Differential Expression of IgM and IgD Discriminates Two Subpopulations of Human Circulating IgM+IgD+CD27+ B Cells That Differ Phenotypically, Functionally, and Genetically.Front Immunol. 2020 May 6;11:736. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.00736. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32435242 Free PMC article.
-
IgM+IgD- B cells in human gut-associated lymphoid tissue have memory features and give rise to IgM+ and IgA+ antibody-secreting cells.Sci Rep. 2025 Jul 22;15(1):26613. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-11209-1. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40695977 Free PMC article.
-
[IgM+IgD+CD27+ B cells in human: an essential role in the protection against encapsulated bacteria].Med Sci (Paris). 2015 Jun-Jul;31(6-7):647-53. doi: 10.1051/medsci/20153106018. Epub 2015 Jul 7. Med Sci (Paris). 2015. PMID: 26152169 Review. French.
-
Memory B cells and CD27.Histol Histopathol. 2000 Apr;15(2):573-6. doi: 10.14670/HH-15.573. Histol Histopathol. 2000. PMID: 10809378 Review.
Cited by
-
High-throughput immunoglobulin repertoire analysis distinguishes between human IgM memory and switched memory B-cell populations.Blood. 2010 Aug 19;116(7):1070-8. doi: 10.1182/blood-2010-03-275859. Epub 2010 May 10. Blood. 2010. PMID: 20457872 Free PMC article.
-
Humoral immunity in humanized mice: a work in progress.J Infect Dis. 2013 Nov;208 Suppl 2(Suppl 2):S155-9. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jit448. J Infect Dis. 2013. PMID: 24151323 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Human B cell memory.Curr Opin Immunol. 2009 Jun;21(3):298-304. doi: 10.1016/j.coi.2009.05.019. Epub 2009 Jun 6. Curr Opin Immunol. 2009. PMID: 19497721 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Activation of B cells by non-canonical helper signals.EMBO Rep. 2012 Sep;13(9):798-810. doi: 10.1038/embor.2012.111. Epub 2012 Aug 7. EMBO Rep. 2012. PMID: 22868664 Free PMC article. Review.
-
IgA natural antibodies are produced following T-cell independent B-cell activation following stroke.Brain Behav Immun. 2021 Jan;91:578-586. doi: 10.1016/j.bbi.2020.09.014. Epub 2020 Sep 19. Brain Behav Immun. 2021. PMID: 32956832 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Klein, U., K. Rajewsky, and R. Kuppers. 1998. Human immunoglobulin (Ig)M+IgD+ peripheral blood B cells expressing the CD27 cell surface antigen carry somatically mutated variable region genes: CD27 as a general marker for somatically mutated (memory) B cells. J. Exp. Med. 188:1679–1689. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Klein, U., R. Kuppers, and K. Rajewsky. 1997. Evidence for a large compartment of IgM-expressing memory B cells in humans. Blood. 89:1288–1298. - PubMed
-
- van Es, J.H., F.H. Meyling, and T. Logtenberg. 1992. High frequency of somatically mutated IgM molecules in the human adult blood B cell repertoire. Eur. J. Immunol. 22:2761–2764. - PubMed
-
- Weller, S., M.C. Braun, B.K. Tan, A. Rosenwald, C. Cordier, M.E. Conley, A. Plebani, D.S. Kumararatne, D. Bonnet, O. Tournilhac, et al. 2004. Human blood IgM “memory” B cells are circulating splenic marginal zone B cells harboring a prediversified immunoglobulin repertoire. Blood. 104:3647–3654. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

