The identification of an osteoclastogenesis inhibitor through the inhibition of glyoxalase I
- PMID: 18695250
- PMCID: PMC2575282
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0712239105
The identification of an osteoclastogenesis inhibitor through the inhibition of glyoxalase I
Abstract
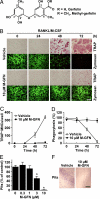
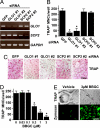
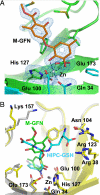
Osteoclasts, bone-resorptive multinucleated cells derived from hematopoietic stem cells, are associated with many bone-related diseases, such as osteoporosis. Osteoclast-targeting small-molecule inhibitors are valuable tools for studying osteoclast biology and for developing antiresorptive agents. Here, we have discovered that methyl-gerfelin (M-GFN), the methyl ester of the natural product gerfelin, suppresses osteoclastogenesis. By using M-GFN-immobilized beads, glyoxalase I (GLO1) was identified as an M-GFN-binding protein. GLO1 knockdown and treatment with an established GLO1 inhibitor in osteoclast progenitor cells interfered with osteoclast generation, suggesting that GLO1 activity is required for osteoclastogenesis. In cells, GLO1 plays a critical role in the detoxification of 2-oxoaldehydes, such as methylglyoxal. M-GFN inhibited the enzymatic activity of GLO1 in vitro and in situ. Furthermore, the cocrystal structure of the GLO1/M-GFN complex revealed the binding mode of M-GFN at the active site of GLO1. These results suggest that M-GFN targets GLO1, resulting in the inhibition of osteoclastogenesis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

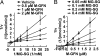
References
-
- Boyle WJ, Simonet WS, Lacey DL. Osteoclast differentiation and activation. Nature. 2003;423:337–342. - PubMed
-
- Suda T, et al. Modulation of osteoclast differentiation and function by the new members of the tumor necrosis factor receptor and ligand families. Endocr Rev. 1999;20:345–357. - PubMed
-
- Hofbauer LC, Neubauer A, Heufelder AE. Receptor activator of nuclear factor-κB ligand and osteoprotegerin: Potential implications for the pathogenesis and treatment of malignant bone diseases. Cancer. 2001;92:460–470. - PubMed
-
- Rogers MJ. New insights into the molecular mechanisms of action of bisphosphonates. Curr Pharmacol Des. 2003;9:2643–2658. - PubMed
-
- Orcel P, Denne MA, de Vernejoul MC. Cyclosporin-A in vitro decreases bone resorption, osteoclast formation, and the fusion of cells of the monocyte-macrophage lineage. Endocrinology. 1991;128:1638–1646. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

