Identification of a vesicular aspartate transporter
- PMID: 18695252
- PMCID: PMC2575331
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0804015105
Identification of a vesicular aspartate transporter
Abstract
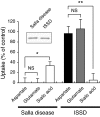
Aspartate is an excitatory amino acid that is costored with glutamate in synaptic vesicles of hippocampal neurons and synaptic-like microvesicles (SLMVs) of pinealocytes and is exocytosed and stimulates neighboring cells by binding to specific cell receptors. Although evidence increasingly supports the occurrence of aspartergic neurotransmission, this process is still debated because the mechanism for the vesicular storage of aspartate is unknown. Here, we show that sialin, a lysosomal H(+)/sialic acid cotransporter, is present in hippocampal synaptic vesicles and pineal SLMVs. RNA interference of sialin expression decreased exocytosis of aspartate and glutamate in pinealocytes. Proteoliposomes containing purified sialin actively accumulated aspartate and glutamate to a similar extent when inside positive membrane potential is imposed as the driving force. Sialin carrying a mutation found in people suffering from Salla disease (R39C) was completely devoid of aspartate and glutamate transport activity, although it retained appreciable H(+)/sialic acid cotransport activity. These results strongly suggest that sialin possesses dual physiological functions and acts as a vesicular aspartate/glutamate transporter. It is possible that people with Salla disease lose aspartergic (and also the associated glutamatergic) neurotransmission, and this could provide an explanation for why Salla disease causes severe neurological defects.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Maycox PR, Hell JW, Jahn R. Amino acid neurotransmission: Spotlight on synaptic vesicles. Trends Neurosci. 1990;13:83–87. - PubMed
-
- Schuldiner S, Shirvan A, Linial M. Vesicular neurotransmitter transporters: From bacteria to humans. Physiol Rev. 1995;75:369–392. - PubMed
-
- Gasnier B. The SLC32 transporter, a key protein for the synaptic release of inhibitory amino acids. Pflügers Arch. 2004;447:756–759. - PubMed
-
- Reimer RJ, Edwards RH. Organic anion transport is the primary function of the SLC17/type I phosphate transporter family. Pflügers Arch. 2004;447:629–635. - PubMed
-
- Bliss TVP, Collingridge GL. A synaptic model of memory: Long-term potentiation in the hippocampus. Nature. 1993;361:31–39. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

