Inhibitory activity of the novel CB2 receptor agonist, GW833972A, on guinea-pig and human sensory nerve function in the airways
- PMID: 18695648
- PMCID: PMC2579660
- DOI: 10.1038/bjp.2008.298
Inhibitory activity of the novel CB2 receptor agonist, GW833972A, on guinea-pig and human sensory nerve function in the airways
Abstract
Background and purpose: Sensory nerves regulate central and local reflexes such as airway plasma protein leakage, bronchoconstriction and cough. Sensory nerve activity may be enhanced during inflammation such that these protective effects become exacerbated and deleterious. Cannabinoids are known to inhibit airway sensory nerve function. However, there is still controversy surrounding which receptor is involved in eliciting these effects.
Experimental approach: We have adopted a pharmacological approach, including using a novel, more selective CB(2) receptor agonist, GW 833972A (1000-fold selective CB(2)/CB(1)), and receptor selective antagonists to investigate the inhibitory activity of cannabinoids on sensory nerve activity in vitro and in vivo in guinea-pig models of cough and plasma extravasation.
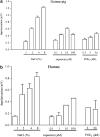
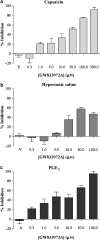
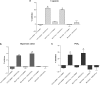
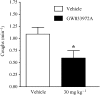
Key results: GW 833972A inhibited capsaicin-induced depolarization of the human and guinea-pig and prostaglandin E(2) (PGE(2)) and hypertonic saline-induced depolarization of the guinea-pig isolated vagus nerve in vitro. GW 833972A also inhibited citric acid-induced cough but not plasma extravasation in the guinea-pig and this effect was blocked by a CB(2) receptor antagonist.
Conclusions and implications: This confirms and extends previous studies highlighting the role of CB(2) receptors in the modulation of sensory nerve activity elicited both by the exogenous ligands capsaicin and hypertonic saline but also by endogenous modulators such as PGE(2) and low pH stimuli. These data establish the CB(2) receptor as an interesting target for the treatment of chronic cough.
Figures

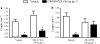
Similar articles
-
Inhibition of guinea-pig and human sensory nerve activity and the cough reflex in guinea-pigs by cannabinoid (CB2) receptor activation.Br J Pharmacol. 2003 Sep;140(2):261-8. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0705435. Epub 2003 Aug 4. Br J Pharmacol. 2003. PMID: 12970104 Free PMC article.
-
Cannabinoid CB(2) receptor activation prevents bronchoconstriction and airway oedema in a model of gastro-oesophageal reflux.Eur J Pharmacol. 2007 Nov 14;573(1-3):206-13. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2007.06.040. Epub 2007 Jul 3. Eur J Pharmacol. 2007. PMID: 17643417
-
CB2 cannabinoid receptor agonist selectively inhibits the mechanosensitivity of mucosal afferents in the guinea pig bladder.Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2021 May 1;320(5):F859-F865. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00065.2021. Epub 2021 Mar 22. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2021. PMID: 33749323
-
Mechanisms of citric acid-induced bronchoconstriction.Am J Med. 2001 Dec 3;111 Suppl 8A:18S-24S. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9343(01)00816-6. Am J Med. 2001. PMID: 11749919 Review.
-
Physiology and plasticity of putative cough fibres in the Guinea pig.Pulm Pharmacol Ther. 2002;15(3):193-8. doi: 10.1006/pupt.2002.0362. Pulm Pharmacol Ther. 2002. PMID: 12099763 Review.
Cited by
-
An advanced recording and analysis system for the differentiation of guinea pig cough responses to citric acid and prostaglandin E2 in real time.PLoS One. 2019 May 22;14(5):e0217366. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0217366. eCollection 2019. PLoS One. 2019. PMID: 31116792 Free PMC article.
-
Tiotropium modulates transient receptor potential V1 (TRPV1) in airway sensory nerves: A beneficial off-target effect?J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2014 Mar;133(3):679-87.e9. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2013.12.003. Epub 2014 Feb 5. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2014. PMID: 24506933 Free PMC article.
-
Peripheral sensory neuron CB2 cannabinoid receptors are necessary for both CB2-mediated antinociceptive efficacy and sparing of morphine tolerance in a mouse model of anti-retroviral toxic neuropathy.Pharmacol Res. 2023 Jan;187:106560. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2022.106560. Epub 2022 Nov 20. Pharmacol Res. 2023. PMID: 36417942 Free PMC article.
-
Cannabinoids pharmacological effects are beyond the palliative effects: CB2 cannabinoid receptor agonist induced cytotoxicity and apoptosis in human colorectal cancer cells (HT-29).Mol Cell Biochem. 2021 Sep;476(9):3285-3301. doi: 10.1007/s11010-021-04158-6. Epub 2021 Apr 22. Mol Cell Biochem. 2021. PMID: 33886060
-
TRPA1 agonists evoke coughing in guinea pig and human volunteers.Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2009 Dec 1;180(11):1042-7. doi: 10.1164/rccm.200905-0665OC. Epub 2009 Sep 3. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2009. PMID: 19729665 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Barnes PJ. Neurogenic inflammation in the airways. Respir Physiol. 2001;125:145–154. - PubMed
-
- Barnes PJ, Baraniuk JN, Belvisi MG. Neuropeptides in the respiratory tract. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1991;144:1187–1198. - PubMed
-
- Belvisi MG. Overview of the innervation of the lung. Curr Opin Pharmacol. 2002;2:211–215. - PubMed
-
- Belvisi MG. Sensory nerves and airway inflammation: role of Aδ and C-fibres. Pulm Pharmacol Ther. 2003;16:1–7. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

