The cardiac sodium channel mutation delQKP 1507-1509 is associated with the expanding phenotypic spectrum of LQT3, conduction disorder, dilated cardiomyopathy, and high incidence of youth sudden death
- PMID: 18697752
- PMCID: PMC2573028
- DOI: 10.1093/europace/eun202
The cardiac sodium channel mutation delQKP 1507-1509 is associated with the expanding phenotypic spectrum of LQT3, conduction disorder, dilated cardiomyopathy, and high incidence of youth sudden death
Abstract
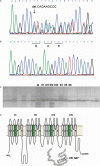
Aim: We report diverse phenotypic consequences of the delQKP-1507-1509 cardiac sodium channel mutation in three generations of a Chinese family.
Methods and results: Clinical and electrocardiographic (ECG), echocardiographic examination was followed by direct sequencing of SCN5A, KCNQ1, HERG, and LAMIN A/C to screen genomic DNA from blood samples. Of two mutation carriers, the proband was born with conduction disorders including second-degree atrioventricular (AV) block with prolonged QTc interval, additionally showing left anterior fascicular block (LAFB), incomplete right bundle-branch block (IRBBB), and intermittent third-degree AV block at 2 years, and clinical presentations of multiple syncope despite normal electroencephalograms at 8 years. Continuous ECG monitoring following presentation at 13 years revealed prolonged QTc and biphasic T-waves, multiple episodes of ventricular tachycardia, ventricular fibrillation, and torsades de pointes. Transthoracal echocardiography then revealed left ventricular dilatation and reduced systolic function. Another mutation carrier showed features of long QT syndrome type 3 (LQT3), LAFB, and dilated cardiomyopathy (DCM). Two additional subjects died suddenly at 13 and 33 years.
Conclusion: This data compliments and expands the spectrum of phenotypes resulting from this known gain-of-function mutation, including not only LQT3, cardiac conduction defects, and sudden death but also DCM, hitherto associated with loss-of-function mutations, for the first time.
Figures


Comment in
-
SCN5A overlap syndromes: no end to disease complexity?Europace. 2008 Nov;10(11):1253-5. doi: 10.1093/europace/eun267. Epub 2008 Sep 26. Europace. 2008. PMID: 18820249 No abstract available.
References
-
- Tan HL, Bezzina CR, Smits JP, Verkerk AO, Wilde AA. Genetic control of sodium channel function. Cardiovasc Res. 2003;57:961–73. - PubMed
-
- Akai J, Makita N, Sakurada H, Shirai N, Ueda K, Kitabatake A, et al. A novel SCN5A mutation associated with idiopathic ventricular fibrillation without typical ECG findings of Brugada syndrome. FEBS Lett. 2000;479:29–34. - PubMed
-
- Groenewegen WA, Firouzi M, Bezzina CR, Vliex S, van Langen IM, Sandkuijl L, et al. A cardiac sodium channel mutation cosegregates with a rare connexin40 genotype in familial atrial standstill. Circ Res. 2003;92:14–22. - PubMed
-
- Wang DW, Desai RR, Crotti L, Arnestad M, Insolia R, Pedrazzini M, et al. Cardiac sodium channel dysfunction in sudden infant death syndrome. Circulation. 2007;115:368–76. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

