Both cIAP1 and cIAP2 regulate TNFalpha-mediated NF-kappaB activation
- PMID: 18697935
- PMCID: PMC2575330
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0711122105
Both cIAP1 and cIAP2 regulate TNFalpha-mediated NF-kappaB activation
Abstract
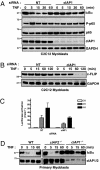
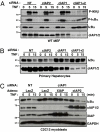
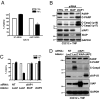
The cellular inhibitor of apoptosis 1 and 2 (cIAP1 and cIAP2) proteins have been implicated in the activation of NF-kappaB by TNFalpha; however, genetic deletion of either cIAP1 or 2 did not support a physiologically relevant role, perhaps because of functional redundancy. To address this, we used combined genetic and siRNA knockdown approaches and report that cIAP1 and 2 are indeed critical, yet redundant, regulators of NF-kappaB activation upon TNFalpha treatment. Whereas NF-kappaB was properly activated by TNFalpha in cultured and primary cells deficient in either cIAP1 or 2, removal of both cIAPs severely blunted its activation. After treatment with TNFalpha, cIAP1 and 2 were rapidly recruited to the TNF receptor 1, along with the adapter protein TNF receptor associated factor 2. Importantly, either cIAP1 or 2 was required for proper TNF receptor 1 signalosome function. In their combined absence, polyubiquitination of receptor interacting protein 1, an upstream event necessary for NF-kappaB signaling, was attenuated. As a result, phosphorylation of the inhibitor of kappaB kinase beta was diminished, and signal transduction was severely blunted. Consequently, cells missing both cIAP1 and 2 were sensitized to TNFalpha-mediated apoptosis. Collectively, these data demonstrate that either cIAP1 or 2 is required for proper Rip1 polyubiquitination and NF-kappaB activation upon TNFalpha treatment.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Liston P, et al. Suppression of apoptosis in mammalian cells by NAIP and a related family of IAP genes. Nature. 1996;379:349–353. - PubMed
-
- Samuel T, et al. Distinct BIR domains of cIAP1 mediate binding to and ubiquitination of tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factor 2 and second mitochondrial activator of caspases. J Biol Chem. 2006;281:1080–1090. - PubMed
-
- Yang Y, Fang S, Jensen JP, Weissman AM, Ashwell JD. Ubiquitin protein ligase activity of IAPs and their degradation in proteasomes in response to apoptotic stimuli. Science. 2000;288:874–877. - PubMed
-
- Eckelman BP, Salvesen GS. The human anti-apoptotic proteins cIAP1 and cIAP2 bind but do not inhibit caspases. J Biol Chem. 2006;281:3254–3260. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

