An intracellular renin-angiotensin system in neurons: fact, hypothesis, or fantasy
- PMID: 18697992
- PMCID: PMC2538674
- DOI: 10.1152/physiol.00002.2008
An intracellular renin-angiotensin system in neurons: fact, hypothesis, or fantasy
Abstract
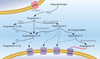
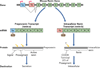
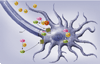
The renin-angiotensin system in the brain acts to regulate a number of physiological processes. Evidence suggests that angiotensin peptides may act as neurotransmitters, although their biosynthetic pathways are poorly understood. We review evidence for neuronal production of angiotensin peptides and hypothesize that angiotensin may be synthesized intracellularly in neurons.
Figures
References
-
- Allen AM, Dosanjh JK, Erac M, Dassanayake S, Hannan RD, Thomas WG. Expression of Constitutively Active Angiotensin Receptors in the Rostral Ventrolateral Medulla Increases Blood Pressure. Hypertension. 2006;47:1054–1061. - PubMed
-
- Aronsson M, Almasan K, Fuxe K, Cintra A, Harfstrand A, Gustafsson JA, Ganten D. Evidence for the existence of angiotensinogen mRNA in magnocellular paraventricular hypothalamic neurons. Acta Physiol Scand. 1988;132:585–586. - PubMed
-
- Bickerton RK, Buckley JP. Evidence for a central mechanism in angiotensin-induced hypertension. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1961;106:834–837.
-
- Cooper JR, Bloom FE, Roth RH. Biochemical basis of neuropharmacology. Oxford: University Press; 1996.
-
- Deschepper CF, Bouhnik J, Ganong WF. Colocalization of angiotensinogen and glial fibrillary acidic protein in astrocytes in rat brain. Brain Res. 1986;374:195–198. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

