Estrogens and neuroprotection in retinal diseases
- PMID: 18698377
- PMCID: PMC2507727
Estrogens and neuroprotection in retinal diseases
Retraction in
-
Full retraction of Kumar DM, Simpkins JW, Agarwal N. Estrogens and neuroprotection in retinal diseases. Mol Vis. 2008;14:1480-6. Review.Mol Vis. 2008;14:2204. Mol Vis. 2008. PMID: 19192491 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
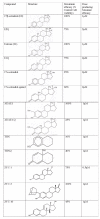
Estrogens play a critical role in the normal growth and development of humans and in recent years our understanding of their effects in the central nervous system (CNS) have been advancing rapidly. It is now known that estrogens influence synaptic plasticity, brain development, and memory. In addition, estrogens have been shown to be neuroprotective in degenerative disorders. The understanding of the influences of estrogens in the retina, as a component of the CNS, has not kept pace with the advances in understanding of the brain. Studies that have addressed the effects of estrogens on the retina, specifically those focusing on glaucoma, are examined here in the hope that estrogen therapy may be a viable option for treating retinal dystrophies and optic neuropathies.
Figures
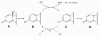
References
-
- Wygnanski T, Desatnik H, Quigley HA, Glovinsky Y. Comparison of ganglion cell loss and cone loss in experimental glaucoma. Am J Ophthalmol. 1995;120:184–9. - PubMed
-
- Van Buskirk EM, Cioffi GA. Glaucomatous optic neuropathy. Am J Ophthalmol. 1992;113:447–52. - PubMed
-
- Javitt JC. Ambulatory visits for eye care by Medicare beneficiaries. Arch Ophthalmol. 1994;112:1025. - PubMed
-
- Javitt JC, Zhou Z, Willke RJ. Association between vision loss and higher medical care costs in Medicare beneficiaries costs are greater for those with progressive vision loss. Ophthalmology. 2007;114:238–45. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
