Identification of c-Src tyrosine kinase substrates using mass spectrometry and peptide microarrays
- PMID: 18698806
- PMCID: PMC2646669
- DOI: 10.1021/pr800198w
Identification of c-Src tyrosine kinase substrates using mass spectrometry and peptide microarrays
Abstract
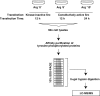
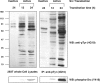
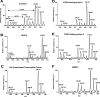
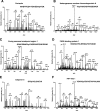
c-Src tyrosine kinase plays a critical role in signal transduction downstream of growth factor receptors, integrins and G protein-coupled receptors. We used stable isotope labeling with amino acids in cell culture (SILAC) approach to identify additional substrates of c-Src tyrosine kinase in human embryonic kidney 293T cells. We have identified 10 known substrates and interactors of c-Src and Src family kinases along with 26 novel substrates. We have experimentally validated 4 of the novel proteins (NICE-4, RNA binding motif 10, FUSE-binding protein 1 and TRK-fused gene) as direct substrates of c-Src using in vitro kinase assays and cotransfection experiments. Significantly, using a c-Src specific inhibitor, we were also able to implicate 3 novel substrates (RNA binding motif 10, EWS1 and Bcl-2 associated transcription factor) in PDGF signaling. Finally, to identify the exact tyrosine residues that are phosphorylated by c-Src on the novel c-Src substrates, we designed custom peptide microarrays containing all possible tyrosine-containing peptides (312 unique peptides) and their mutant counterparts containing a Tyr --> Phe substitution from 14 of the identified substrates. Using this platform, we identified 34 peptides that are phosphorylated by c-Src. We have demonstrated that SILAC-based quantitative proteomics approach is suitable for identification of substrates of nonreceptor tyrosine kinases and can be coupled with peptide microarrays for high-throughput identification of substrate phosphopeptides.
Figures

References
-
- Thomas S. M.; Brugge J. S. Cellular functions regulated by Src family kinases. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 1997, 13, 513–609. - PubMed
-
- Olsen J. V.; Blagoev B.; Gnad F.; Macek B.; Kumar C.; Mortensen P.; Mann M. Global, in vivo, and site-specific phosphorylation dynamics in signaling networks. Cell 2006, 127, 635–648. - PubMed
-
- Ficarro S. B.; McCleland M. L.; Stukenberg P. T.; Burke D. J.; Ross M. M.; Shabanowitz J.; Hunt D. F.; White F. M. Phosphoproteome analysis by mass spectrometry and its application to Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Nat. Biotechnol. 2002, 20, 301–305. - PubMed
-
- Beausoleil S. A.; Villen J.; Gerber S. A.; Rush J.; Gygi S. P. A probability-based approach for high-throughput protein phosphorylation analysis and site localization. Nat. Biotechnol. 2006, 24, 1285–1292. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

