Activated Akt1 accelerates MMTV-c-ErbB2 mammary tumourigenesis in mice without activation of ErbB3
- PMID: 18700973
- PMCID: PMC2575543
- DOI: 10.1186/bcr2132
Activated Akt1 accelerates MMTV-c-ErbB2 mammary tumourigenesis in mice without activation of ErbB3
Abstract
Introduction: ErbB2, a member of the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) family, is overexpressed in 20% to 30% of human breast cancer cases and forms oncogenic signalling complexes when dimerised to ErbB3 or other EGFR family members.
Methods: We crossed mouse mammary tumour virus (MMTV)-myr-Akt1 transgenic mice (which express constitutively active Akt1 in the mammary gland) with MMTV-c-ErbB2 transgenic mice to evaluate the role of Akt1 activation in ErbB2-induced mammary carcinoma using immunoblot analysis, magnetic resonance spectroscopy and histological analyses.
Results: Bitransgenic MMTV-c-ErbB2, MMTV-myr-Akt1 mice develop mammary tumours twice as fast as MMTV-c-ErbB2 mice. The bitransgenic tumours were less organised, had more mitotic figures and fewer apoptotic cells. However, many bitransgenic tumours displayed areas of extensive necrosis compared with tumours from MMTV-c-ErbB2 mice. The two tumour types demonstrate dramatically different expression and activation of EGFR family members, as well as different metabolic profiles. c-ErbB2 tumours demonstrate overexpression of EGFR, ErbB2, ErbB3 and ErbB4, and activation/phosphorylation of both ErbB2 and ErbB3, underscoring the importance of the entire EGFR family in ErbB2-induced tumourigenesis. Tumours from bitransgenic mice overexpress the myr-Akt1 and ErbB2 transgenes, but there was dramatically less overexpression and phosphorylation of ErbB3, diminished phosphorylation of ErbB2, decreased level of EGFR protein and undetectable ErbB4 protein. There was also an observable attenuation in a subset of tyrosine-phosphorylated secondary signalling molecules in the bitransgenic tumours compared with c-ErbB2 tumours, but Erk was activated/phosphorylated in both tumour types. Finally, the bitransgenic tumours were metabolically more active as indicated by increased glucose transporter 1 (GLUT1) expression, elevated lactate production and decreased intracellular glucose (suggesting increased glycolysis).
Conclusion: Expression of activated Akt1 in MMTV-c-ErbB2 mice accelerates tumourigenesis with a reduced requirement for signalling through the EGFR family, as well as a reduced requirement for a subset of downstream signaling molecules with a metabolic shift in the tumours from bitransgenic mice. The reduction in signalling downstream of ErbB2 when Akt is activated suggest a possible mechanism by which tumour cells can become resistant to ErbB2-targeted therapies, necessitating therapies that target oncogenic signalling events downstream of ErbB2.
Figures


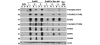
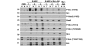


Similar articles
-
Functional interaction between mouse erbB3 and wild-type rat c-neu in transgenic mouse mammary tumor cells.Breast Cancer Res. 2005;7(5):R708-18. doi: 10.1186/bcr1281. Epub 2005 Jul 6. Breast Cancer Res. 2005. PMID: 16168116 Free PMC article.
-
Increased erbB3 promotes erbB2/neu-driven mammary tumor proliferation and co-targeting of erbB2/erbB3 receptors exhibits potent inhibitory effects on breast cancer cells.Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2015 Jun 1;8(6):6143-56. eCollection 2015. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2015. PMID: 26261492 Free PMC article.
-
Activation of Akt1 accelerates carcinogen-induced tumorigenesis in mammary gland of virgin and post-lactating transgenic mice.BMC Cancer. 2014 Apr 17;14:266. doi: 10.1186/1471-2407-14-266. BMC Cancer. 2014. PMID: 24742286 Free PMC article.
-
ERBB3/HER3 and ERBB2/HER2 duet in mammary development and breast cancer.J Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia. 2008 Jun;13(2):215-23. doi: 10.1007/s10911-008-9083-7. Epub 2008 May 3. J Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia. 2008. PMID: 18454306 Free PMC article. Review.
-
EGFR family: structure physiology signalling and therapeutic targets.Growth Factors. 2008 Oct;26(5):263-74. doi: 10.1080/08977190802312844. Growth Factors. 2008. PMID: 18800267 Review.
Cited by
-
A Systematic Review of miR-29 in Cancer.Mol Ther Oncolytics. 2018 Dec 31;12:173-194. doi: 10.1016/j.omto.2018.12.011. eCollection 2019 Mar 29. Mol Ther Oncolytics. 2018. PMID: 30788428 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Modulation of glucose transporter 1 (GLUT1) expression levels alters mouse mammary tumor cell growth in vitro and in vivo.PLoS One. 2011;6(8):e23205. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0023205. Epub 2011 Aug 3. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 21826239 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA-29B (mir-29b) regulates the Warburg effect in ovarian cancer by targeting AKT2 and AKT3.Oncotarget. 2015 Dec 1;6(38):40799-814. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.5695. Oncotarget. 2015. PMID: 26512921 Free PMC article.
-
Function, regulation and pathological roles of the Gab/DOS docking proteins.Cell Commun Signal. 2009 Sep 8;7:22. doi: 10.1186/1478-811X-7-22. Cell Commun Signal. 2009. PMID: 19737390 Free PMC article.
-
Genetically engineered mouse models of PI3K signaling in breast cancer.Mol Oncol. 2013 Apr;7(2):146-64. doi: 10.1016/j.molonc.2013.02.003. Epub 2013 Feb 11. Mol Oncol. 2013. PMID: 23478237 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

