Selective roles for cholesterol and actin in compartmentalization of different proteins in the Golgi and plasma membrane of polarized cells
- PMID: 18701450
- PMCID: PMC2662031
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M803819200
Selective roles for cholesterol and actin in compartmentalization of different proteins in the Golgi and plasma membrane of polarized cells
Erratum in
- J Biol Chem. 2009 Jan 2;284(1):708
Abstract
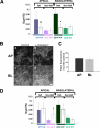
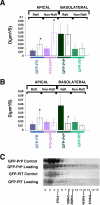
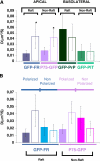
To determine the roles of cholesterol and the actin cytoskeleton in apical and basolateral protein organization and sorting, we have performed comprehensive confocal fluorescence recovery after photobleaching analyses of apical and basolateral and raft- and non-raft-associated proteins, both at the plasma membrane and in the Golgi apparatus of polarized MDCK cells. We show that at both the apical and basolateral plasma membrane domains, raft-associated proteins diffuse faster than non-raft-associated proteins and that, different from the latter, they become restricted upon depletion of cholesterol. Furthermore, only transmembrane apical proteins are restricted by the actin network. This indicates that cholesterol-dependent domains exist both at the apical and basolateral membranes of polarized cells and that the actin cytoskeleton has a predominant role in the organization of transmembrane proteins independent of their association with rafts at the apical membrane. In the Golgi apparatus apical proteins appear to be segregated from the basolateral ones in a compartment that is sensitive both to cholesterol depletion and actin rearrangements. Furthermore, consistent with the role of actin rearrangements in apical protein sorting, we found that apical proteins exhibit a differential sensitivity to actin depolymerization in the Golgi of polarized and nonpolarized cells.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Transcytotic efflux from early endosomes is dependent on cholesterol and glycosphingolipids in polarized hepatic cells.Mol Biol Cell. 2003 Jul;14(7):2689-705. doi: 10.1091/mbc.e02-12-0816. Epub 2003 Apr 4. Mol Biol Cell. 2003. PMID: 12857857 Free PMC article.
-
Polarized sorting in epithelial cells: raft clustering and the biogenesis of the apical membrane.J Cell Sci. 2004 Dec 1;117(Pt 25):5955-64. doi: 10.1242/jcs.01596. J Cell Sci. 2004. PMID: 15564373 Review.
-
Trafficking of cholera toxin-ganglioside GM1 complex into Golgi and induction of toxicity depend on actin cytoskeleton.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2004 Nov;287(5):C1453-62. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00189.2004. Epub 2004 Aug 4. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2004. PMID: 15294854
-
Tetraspanin CD82 controls the association of cholesterol-dependent microdomains with the actin cytoskeleton in T lymphocytes: relevance to co-stimulation.J Cell Sci. 2004 Oct 15;117(Pt 22):5269-82. doi: 10.1242/jcs.01380. Epub 2004 Sep 28. J Cell Sci. 2004. PMID: 15454569
-
Glycosylphosphatidylinositol-anchored proteins: Membrane organization and transport.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2016 Apr;1858(4):632-9. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamem.2015.12.018. Epub 2015 Dec 17. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2016. PMID: 26706096 Review.
Cited by
-
Apical trafficking in epithelial cells: signals, clusters and motors.J Cell Sci. 2009 Dec 1;122(Pt 23):4253-66. doi: 10.1242/jcs.032615. J Cell Sci. 2009. PMID: 19923269 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Fat-induced membrane cholesterol accrual provokes cortical filamentous actin destabilisation and glucose transport dysfunction in skeletal muscle.Diabetologia. 2012 Feb;55(2):457-67. doi: 10.1007/s00125-011-2334-y. Epub 2011 Oct 15. Diabetologia. 2012. PMID: 22002007 Free PMC article.
-
GPI-anchored proteins are confined in subdiffraction clusters at the apical surface of polarized epithelial cells.Biochem J. 2017 Dec 1;474(24):4075-4090. doi: 10.1042/BCJ20170582. Biochem J. 2017. PMID: 29046391 Free PMC article.
-
Up-regulation of the ATP-binding cassette transporter A1 inhibits hepatitis C virus infection.PLoS One. 2014 Mar 19;9(3):e92140. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0092140. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24646941 Free PMC article.
-
Imaging of mobile long-lived nanoplatforms in the live cell plasma membrane.J Biol Chem. 2010 Dec 31;285(53):41765-71. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.182121. Epub 2010 Oct 21. J Biol Chem. 2010. PMID: 20966075 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

