Cross-talk between LPA1 and epidermal growth factor receptors mediates up-regulation of sphingosine kinase 1 to promote gastric cancer cell motility and invasion
- PMID: 18701480
- PMCID: PMC2763580
- DOI: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-08-0411
Cross-talk between LPA1 and epidermal growth factor receptors mediates up-regulation of sphingosine kinase 1 to promote gastric cancer cell motility and invasion
Abstract
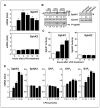
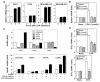
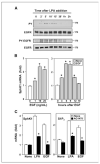
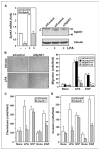
Lysophosphatidic acid (LPA) and sphingosine-1-phosphate (S1P) are lysophospholipid mediators of diverse cellular processes important for cancer progression. S1P is produced by two sphingosine kinases, SphK1 and SphK2. Expression of SphK1 is elevated in many cancers. Here, we report that LPA markedly enhanced SphK1 mRNA and protein in gastric cancer MKN1 cells but had no effect on SphK2. LPA also up-regulated SphK1 expression in other human cancer cells that endogenously express the LPA(1) receptor, such as DLD1 colon cancer cells and MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells, but not in HT29 colon cancer cells or MDA-MB-453 breast cancer cells, which do not express the LPA(1) receptor. An LPA(1) receptor antagonist or down-regulation of its expression prevented SphK1 and S1P(3) receptor up-regulation by LPA. LPA transactivated the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) in these cells, and the EGFR inhibitor AG1478 attenuated the increased SphK1 and S1P(3) expression induced by LPA. Moreover, down-regulation of SphK1 attenuated LPA-stimulated migration and invasion of MNK1 cells yet had no effect on expression of neovascularizing factors, such as interleukin (IL)-8, IL-6, urokinase-type plasminogen activator (uPA), or uPA receptor induced by LPA. Finally, down-regulation of S1P(3), but not S1P(1), also reduced LPA-stimulated migration and invasion of MKN1 cells. Collectively, our results suggest that SphK1 is a convergence point of multiple cell surface receptors for three different ligands, LPA, EGF, and S1P, which have all been implicated in regulation of motility and invasiveness of cancer cells.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Sphingosine-1-phosphate and interleukin-1 independently regulate plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 and urokinase-type plasminogen activator receptor expression in glioblastoma cells: implications for invasiveness.Mol Cancer Res. 2008 Sep;6(9):1469-77. doi: 10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-08-0082. Mol Cancer Res. 2008. PMID: 18819934 Free PMC article.
-
Expression of sphingosine-1-phosphate receptors and lysophosphatidic acid receptors on cultured and xenografted human colon, breast, melanoma, and lung tumor cells.Tumour Biol. 2010 Aug;31(4):341-9. doi: 10.1007/s13277-010-0043-7. Epub 2010 May 18. Tumour Biol. 2010. PMID: 20480410
-
Lysophosphatidate Promotes Sphingosine 1-Phosphate Metabolism and Signaling: Implications for Breast Cancer and Doxorubicin Resistance.Cell Biochem Biophys. 2021 Sep;79(3):531-545. doi: 10.1007/s12013-021-01024-6. Epub 2021 Aug 20. Cell Biochem Biophys. 2021. PMID: 34415509 Free PMC article.
-
Cell surface receptors in lysophospholipid signaling.Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2004 Oct;15(5):457-65. doi: 10.1016/j.semcdb.2004.05.005. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2004. PMID: 15271291 Review.
-
Targeting sphingosine-1-phosphate in hematologic malignancies.Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2011 Nov;11(9):794-8. doi: 10.2174/187152011797655122. Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2011. PMID: 21707492 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Lysophosphatidic Acid-Induced EGFR Transactivation Promotes Gastric Cancer Cell DNA Replication by Stabilizing Geminin in the S Phase.Front Pharmacol. 2021 Sep 29;12:706240. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.706240. eCollection 2021. Front Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34658851 Free PMC article.
-
Lysophosphatidic Acid Receptor Antagonists and Cancer: The Current Trends, Clinical Implications, and Trials.Cells. 2021 Jun 29;10(7):1629. doi: 10.3390/cells10071629. Cells. 2021. PMID: 34209775 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting sphingosine kinase 1 (SK1) enhances oncogene-induced senescence through ceramide synthase 2 (CerS2)-mediated generation of very-long-chain ceramides.Cell Death Dis. 2021 Jan 4;12(1):27. doi: 10.1038/s41419-020-03281-4. Cell Death Dis. 2021. PMID: 33414460 Free PMC article.
-
Estradiol induces export of sphingosine 1-phosphate from breast cancer cells via ABCC1 and ABCG2.J Biol Chem. 2010 Apr 2;285(14):10477-86. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M109.064162. Epub 2010 Jan 28. J Biol Chem. 2010. PMID: 20110355 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting Sphingosine-1-Phosphate Signaling in Breast Cancer.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Mar 15;25(6):3354. doi: 10.3390/ijms25063354. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38542328 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Murph M, Tanaka T, Liu S, et al. Of spiders and crabs: the emergence of lysophospholipids and their metabolic pathways as targets for therapy in cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2006;12:6598–602. - PubMed
-
- Alvarez SE, Milstien S, Spiegel S. Autocrine and paracrine roles of sphingosine-1-phosphate. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2007;18:300–7. - PubMed
-
- Gardell SE, Dubin AE, Chun J. Emerging medicinal roles for lysophospholipid signaling. Trends Mol Med. 2006;12:65–75. - PubMed
-
- Parkin DM. Global cancer statistics in the year 2000. Lancet Oncol. 2001;2:533–43. - PubMed
-
- Shida D, Kitayama J, Yamaguchi H, et al. Dual mode regulation of migration by lysophosphatidic acid in human gastric cancer cells. Exp Cell Res. 2004;301:168–78. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

