Focal gains of VEGFA and molecular classification of hepatocellular carcinoma
- PMID: 18701503
- PMCID: PMC2587454
- DOI: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-08-0742
Focal gains of VEGFA and molecular classification of hepatocellular carcinoma
Abstract
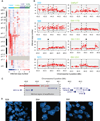
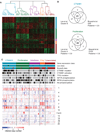
Hepatocellular carcinomas represent the third leading cause of cancer-related deaths worldwide. The vast majority of cases arise in the context of chronic liver injury due to hepatitis B virus or hepatitis C virus infection. To identify genetic mechanisms of hepatocarcinogenesis, we characterized copy number alterations and gene expression profiles from the same set of tumors associated with hepatitis C virus. Most tumors harbored 1q gain, 8q gain, or 8p loss, with occasional alterations in 13 additional chromosome arms. In addition to amplifications at 11q13 in 6 of 103 tumors, 4 tumors harbored focal gains at 6p21 incorporating vascular endothelial growth factor A (VEGFA). Fluorescence in situ hybridization on an independent validation set of 210 tumors found 6p21 high-level gains in 14 tumors, as well as 2 tumors with 6p21 amplifications. Strikingly, this locus overlapped with copy gains in 4 of 371 lung adenocarcinomas. Overexpression of VEGFA via 6p21 gain in hepatocellular carcinomas suggested a novel, non-cell-autonomous mechanism of oncogene activation. Hierarchical clustering of gene expression among 91 of these tumors identified five classes, including "CTNNB1", "proliferation", "IFN-related", a novel class defined by polysomy of chromosome 7, and an unannotated class. These class labels were further supported by molecular data; mutations in CTNNB1 were enriched in the "CTNNB1" class, whereas insulin-like growth factor I receptor and RPS6 phosphorylation were enriched in the "proliferation" class. The enrichment of signaling pathway alterations in gene expression classes provides insights on hepatocellular carcinoma pathogenesis. Furthermore, the prevalence of VEGFA high-level gains in multiple tumor types suggests indications for clinical trials of antiangiogenic therapies.
Conflict of interest statement
Please see Author Conflict of Interest forms for complete list. None of these companies had any role in the study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.
Figures


References
-
- Thorgeirsson SS, Grisham JW. Molecular pathogenesis of human hepatocellular carcinoma. Nat Genet. 2002;31:339–346. - PubMed
-
- Farazi PA, DePinho RA. Hepatocellular carcinoma pathogenesis: from genes to environment. Nat Rev Cancer. 2006;6:674–687. - PubMed
-
- Breuhahn K, Vreden S, Haddad R, et al. Molecular profiling of human hepatocellular carcinoma defines mutually exclusive interferon regulation and insulin-like growth factor II overexpression. Cancer Res. 2004;64:6058–6064. - PubMed
-
- Lee JS, Chu IS, Heo J, et al. Classification and prediction of survival in hepatocellular carcinoma by gene expression profiling. Hepatology. 2004;40:667–676. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

