Loss of PINK1 function affects development and results in neurodegeneration in zebrafish
- PMID: 18701682
- PMCID: PMC6670558
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0979-08.2008
Loss of PINK1 function affects development and results in neurodegeneration in zebrafish
Abstract
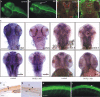
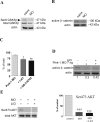
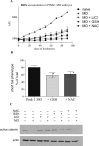
Parkinson's disease (PD) is the second most prevalent neurodegenerative disorder in the Western world. PTEN (phosphatase/tensin homolog on chromosome 10)-induced putative kinase 1 (PINK1), a putative kinase that is mutated in autosomal recessive forms of PD, is also implicated in sporadic cases of the disease. Although the mutations appear to result in a loss of function, the roles of this protein and the pathways involved in PINK1 PD are poorly understood. Here, we generated a vertebrate model of PINK1 insufficiency using morpholino oligonucleotide knockdown in zebrafish (Danio rerio). PINK1 knockdown results in a severe developmental phenotype that is rescued by wild-type human PINK1 mRNA. Morphants display a moderate decrease in the numbers of central dopaminergic neurons and alterations of mitochondrial function, including increases in caspase-3 activity and reactive oxygen species (ROS) levels. When the morphants were exposed to several drugs with antioxidant properties, ROS levels were normalized and the associated phenotype improved. In addition, GSK3beta-related mechanisms can account for some of the effects of PINK1 knockdown, as morphant fish show elevated GSK3beta activity and their phenotype is partially abrogated by GSK3beta inhibitors, such as LiCl and SB216763 [3-(2,4-dichlorophenyl)-4-(1-methyl-1H-indol-3-yl)1H-pyrrole-2,5-dione]. This provides new insights into the biology of PINK1 and a possible therapeutic avenue for further investigation.
Figures



References
-
- Abdelilah S, Mountcastle-Shah E, Harvey M, Solnica-Krezel L, Schier AF, Stemple DL, Malicki J, Neuhauss SC, Zwartkruis F, Stainier DY, Rangini Z, Driever W. Mutations affecting neural survival in the zebrafish Danio rerio. Development. 1996;123:217–227. - PubMed
-
- Blader P, Fischer N, Gradwohl G, Guillemot F, Strähle U. The activity of neurogenin1 is controlled by local cues in the zebrafish embryo. Development. 1997;124:4557–4569. - PubMed
-
- Carmichael J, Sugars KL, Bao YP, Rubinsztein DC. Glycogen synthase kinase-3beta inhibitors prevent cellular polyglutamine toxicity caused by the Huntington's disease mutation. J Biol Chem. 2002;277:33791–33798. - PubMed
-
- Castelo-Branco G, Rawal N, Arenas E. GSK-3beta inhibition/beta-catenin stabilization in ventral midbrain precursors increases differentiation into dopamine neurons. J Cell Sci. 2004;117:5731–5737. - PubMed
-
- Clark IE, Dodson MW, Jiang C, Cao JH, Huh JR, Seol JH, Yoo SJ, Hay BA, Guo M. Drosophila pink1 is required for mitochondrial function and interacts genetically with parkin. Nature. 2006;441:1162–1166. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
