Coexpression of neuronatin splice forms promotes medulloblastoma growth
- PMID: 18701710
- PMCID: PMC2666248
- DOI: 10.1215/15228517-2008-038
Coexpression of neuronatin splice forms promotes medulloblastoma growth
Abstract
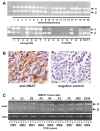
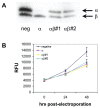
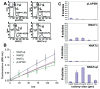
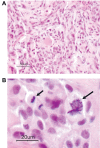
Medulloblastoma (MB) is the most common pediatric brain cancer. Several important developmental pathways have been implicated in MB formation, but fewer therapeutic targets have been identified. To locate frequently overexpressed genes, we performed a comprehensive gene expression survey of MB. Our comparison of 20 primary tumors to normal cerebellum identified neuronatin (NNAT) as the most frequently overexpressed gene in our analysis. NNAT is a neural-specific developmental gene with alpha and beta splice forms. Functional evaluation revealed that RNA interference knockdown of NNAT causes a significant decrease in proliferation. Conversely, coexpression of both splice forms in NNAT-negative MB cell lines increased proliferation, caused a significant shift from G(1) to G(2)/M, and increased soft agar colony formation and size. When expressed individually, each NNAT splice form had much less effect on these in vitro oncogenic predictors. In an in vivo model, the coexpression of both splice forms conferred the ability of xenograft formation to human MB cells that do not normally form xenografts, whereas a control gene had no effect. Our findings suggest that the frequently observed overexpression of both NNAT splice forms in MB enhances growth in this cancer.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Identification of differentially expressed and developmentally regulated genes in medulloblastoma using suppression subtraction hybridization.Oncogene. 2004 Apr 22;23(19):3444-53. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1207475. Oncogene. 2004. PMID: 15064731
-
Neuronatin: a new inflammation gene expressed on the aortic endothelium of diabetic mice.Diabetes. 2008 Oct;57(10):2774-83. doi: 10.2337/db07-1746. Epub 2008 Jun 30. Diabetes. 2008. PMID: 18591389 Free PMC article.
-
Neuronatin Promotes the Progression of Non-small Cell Lung Cancer by Activating the NF-κB Signaling.Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 2024;24(11):1128-1143. doi: 10.2174/0115680096271746240103063325. Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 2024. PMID: 38299400
-
Neuralized1 causes apoptosis and downregulates Notch target genes in medulloblastoma.Neuro Oncol. 2010 Dec;12(12):1244-56. doi: 10.1093/neuonc/noq091. Epub 2010 Sep 16. Neuro Oncol. 2010. PMID: 20847082 Free PMC article.
-
Neuronatin gene: Imprinted and misfolded: Studies in Lafora disease, diabetes and cancer may implicate NNAT-aggregates as a common downstream participant in neuronal loss.Genomics. 2014 Feb-Mar;103(2-3):183-8. doi: 10.1016/j.ygeno.2013.12.001. Epub 2013 Dec 15. Genomics. 2014. PMID: 24345642 Review.
Cited by
-
A serial analysis of gene expression profile of the Alzheimer's disease Tg2576 mouse model.Neurotox Res. 2010 May;17(4):360-79. doi: 10.1007/s12640-009-9112-3. Epub 2009 Sep 16. Neurotox Res. 2010. PMID: 19760337
-
Proteomic Advances in Glial Tumors through Mass Spectrometry Approaches.Medicina (Kaunas). 2019 Jul 27;55(8):412. doi: 10.3390/medicina55080412. Medicina (Kaunas). 2019. PMID: 31357616 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Bio-informatics analysis of a gene co-expression module in adipose tissue containing the diet-responsive gene Nnat.BMC Syst Biol. 2010 Dec 27;4:175. doi: 10.1186/1752-0509-4-175. BMC Syst Biol. 2010. PMID: 21187013 Free PMC article.
-
Dynamic expression patterns of imprinted genes in human embryonic stem cells following prolonged passaging and differentiation.J Assist Reprod Genet. 2011 Apr;28(4):315-23. doi: 10.1007/s10815-010-9524-2. Epub 2010 Dec 16. J Assist Reprod Genet. 2011. PMID: 21161363 Free PMC article.
-
Proteomic and phosphoproteomic comparison of human ES and iPS cells.Nat Methods. 2011 Sep 11;8(10):821-7. doi: 10.1038/nmeth.1699. Nat Methods. 2011. PMID: 21983960 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Raffel C, Jenkins RB, Frederick L, et al. Sporadic medulloblastomas contain PTCH mutations. Cancer Res. 1997;57:842–845. - PubMed
-
- Fan X, Mikolaenko I, Elhassan I, et al. Notch1 and notch2 have opposite effects on embryonal brain tumor growth. Cancer Res. 2004;64:7787–7793. - PubMed
-
- Boon K, Eberhart CG, Riggins G. Genomic amplification of orthodenticle homologue 2 in medulloblastomas. Cancer Res. 2005;65:703–707. - PubMed
-
- Velculescu VE, Zhang L, Vogelstein B, Kinzler KW. Serial analysis of gene expression. Science. 1995;270:484–487. - PubMed
-
- St Croix B, Rago C, Velculescu V, et al. Genes expressed in human tumor endothelium. Science. 2000;289:1197–1202. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

