Transactivation of EGF receptor and ErbB2 protects intestinal epithelial cells from TNF-induced apoptosis
- PMID: 18701712
- PMCID: PMC2575333
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0801463105
Transactivation of EGF receptor and ErbB2 protects intestinal epithelial cells from TNF-induced apoptosis
Abstract
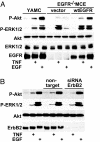
TNF is a pleiotropic cytokine that activates both anti- and proapoptotic signaling pathways, with cell fate determined by the balance between these two pathways. Activation of ErbB family members, including EGF receptor (EGFR/ErbB1), promotes cell survival and regulates several signals that overlap with those stimulated by TNF. This study was undertaken to determine the effects of TNF on EGFR and ErbB2 activation and intestinal epithelial cell survival. Mice, young adult mouse colon epithelial cells, and EGFR knockout mouse colon epithelial cells were treated with TNF. Activation of EGFR, ErbB2, Akt, Src, and apoptosis were determined in vivo and in vitro. TNF stimulated EGFR phosphorylation in young adult mouse colon epithelial cells, and loss of EGFR expression or inhibition of kinase activity increased TNF-induced apoptosis, which was prevented in WT but not by kinase-inactive EGFR expression. Similarly, TNF injection stimulated apoptosis in EGFR-kinase-defective mice (EGFR(wa2)) compared with WT mice. TNF also activated ErbB2, and loss of ErbB2 expression increased TNF-induced apoptosis. Furthermore, Src-kinase activity and the expression of both EGFR and ErbB2 were required for TNF-induced cell survival. Akt was shown to be a downstream target of TNF-activated EGFR and ErbB2. These findings demonstrate that EGFR and ErbB2 are critical mediators of TNF-regulated antiapoptotic signals in intestinal epithelial cells. Given evidence for TNF signaling in the development of colitis-associated carcinoma, this observation has significant implications for understanding the role of EGFR in maintaining intestinal epithelial cell homeostasis during cytokine-mediated inflammatory responses.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
TNF transactivation of EGFR stimulates cytoprotective COX-2 expression in gastrointestinal epithelial cells.Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2011 Aug;301(2):G220-9. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00383.2010. Epub 2011 May 12. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2011. PMID: 21566012 Free PMC article.
-
A Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG-derived soluble protein, p40, stimulates ligand release from intestinal epithelial cells to transactivate epidermal growth factor receptor.J Biol Chem. 2013 Oct 18;288(42):30742-30751. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.492397. Epub 2013 Sep 16. J Biol Chem. 2013. PMID: 24043629 Free PMC article.
-
EGFR plays a pivotal role in the regulation of polyamine-dependent apoptosis in intestinal epithelial cells.Cell Signal. 2007 Dec;19(12):2519-27. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2007.08.001. Epub 2007 Aug 15. Cell Signal. 2007. PMID: 17825525 Free PMC article.
-
Decoding epithelial signals: critical role for the epidermal growth factor receptor in controlling intestinal transport function.Acta Physiol (Oxf). 2009 Jan;195(1):149-59. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.2008.01929.x. Epub 2008 Oct 28. Acta Physiol (Oxf). 2009. PMID: 18983445 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cellular redox: a modulator of intestinal epithelial cell proliferation.News Physiol Sci. 2003 Oct;18:201-4. doi: 10.1152/nips.01448.2003. News Physiol Sci. 2003. PMID: 14500800 Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Early Enteral Administration of a Complex Lipid Emulsion Supplement Prevents Postnatal Deficits in Docosahexaenoic and Arachidonic Acids and Increases Tissue Accretion of Lipophilic Nutrients in Preterm Piglets.JPEN J Parenter Enteral Nutr. 2020 Jan;44(1):69-79. doi: 10.1002/jpen.1697. Epub 2019 Aug 23. JPEN J Parenter Enteral Nutr. 2020. PMID: 31441521 Free PMC article.
-
Claudin-2 expression increases tumorigenicity of colon cancer cells: role of epidermal growth factor receptor activation.Oncogene. 2011 Jul 21;30(29):3234-47. doi: 10.1038/onc.2011.43. Epub 2011 Mar 7. Oncogene. 2011. PMID: 21383692 Free PMC article.
-
Polyethylene glycol diminishes pathological effects of Citrobacter rodentium infection by blocking bacterial attachment to the colonic epithelia.Gut Microbes. 2011 Sep 1;2(5):267-73. doi: 10.4161/gmic.2.5.18256. Epub 2011 Sep 1. Gut Microbes. 2011. PMID: 22067938 Free PMC article.
-
The intestinal epithelial barrier: a therapeutic target?Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2017 Jan;14(1):9-21. doi: 10.1038/nrgastro.2016.169. Epub 2016 Nov 16. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2017. PMID: 27848962 Free PMC article. Review.
-
EGFR inhibits TNF-α-mediated pathway by phosphorylating TNFR1 at tyrosine 360 and 401.Cell Death Differ. 2024 Oct;31(10):1318-1332. doi: 10.1038/s41418-024-01316-3. Epub 2024 May 24. Cell Death Differ. 2024. PMID: 38789573 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hanahan D, Weinberg RA. The hallmarks of cancer. Cell. 2000;100:57–70. - PubMed
-
- Micheau O, Tschopp J. Induction of TNF receptor I-mediated apoptosis via two sequential signaling complexes. Cell. 2003;114:181–190. - PubMed
-
- Yan F, John SK, Polk DB. Kinase suppressor of Ras determines survival of intestinal cells exposed to tumor necrosis factor. Cancer Res. 2001;61:8668–8675. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

