Activation of atypical protein kinase Czeta toward TC10 is regulated by high-fat diet and aerobic exercise in skeletal muscle
- PMID: 18702941
- PMCID: PMC2597576
- DOI: 10.1016/j.metabol.2008.03.023
Activation of atypical protein kinase Czeta toward TC10 is regulated by high-fat diet and aerobic exercise in skeletal muscle
Abstract
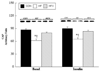
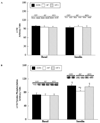
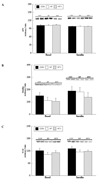
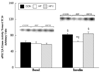
We determined whether sustained aerobic exercise reverses high-fat diet-induced impairments in the c-Cbl associated protein (CAP)/Casitas b-lineage lymphoma (c-Cbl) signaling cascade in rodent skeletal muscle. Sprague-Dawley rats were placed into either control (n = 16) or high-fat-fed (n = 32) diet groups for 4 weeks. During a subsequent 4-week experimental period, 16 high-fat-fed rats remained sedentary, 16 high-fat-fed rats completed 4 weeks of exercise training, and control animals were sedentary and remained on the control diet. After the intervention period, animals were subjected to hind limb perfusions in the presence (n = 8 per group) or absence (n = 8 per group) of insulin. In the plasma membrane fractions, neither high-fat feeding nor exercise training altered adaptor protein with PH and SH2 domains, (APS), c-Cbl, or TC10 protein concentrations. In contrast, CAP protein concentration and insulin-stimulated plasma membrane c-Cbl tyrosine phosphorylation were reduced by high-fat feeding; but exercise training reversed these impairments. Of note was that insulin-stimulated atypical protein kinase Czeta kinase activity toward TC10 was reduced by high-fat feeding but normalized by exercise training. We conclude that sustained (4 weeks) exercise training can reverse high-fat diet-induced impairments on the CAP/c-Cbl pathway in high-fat-fed rodent skeletal muscle. We also provide the first evidence that the CAP/c-Cbl insulin signaling cascade in skeletal muscle may directly interact with components of the classic (phosphoinositide 3-kinase dependent) insulin signaling cascade.
Figures
References
-
- Kanai F, Ito K, Todaka M, Hayashi H, Kamohara SKI, et al. Insulin-stimulated GLUT4 translocation is relevant to the phosphorylation of IRS-1 and the activity of PI3-kinase. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1994;195:762–768. - PubMed
-
- Yeh J-I, Gulve EA, Rameh L, Birnbaum MJ. The effects of wortmannin on rat skeletal muscle. J. Biol. Chem. 1995;270:2107–2111. - PubMed
-
- Terauchi Y, Tsuji T, Satoh S, Minoura H, Murakami K, Okuno A, et al. Increased insulin sensitivity and hypoglycemia in mice lacking p85 alpha subunit of phosphoinositide 3-kinase. Nat. Genet. 1999;21:230–235. - PubMed
-
- Hansen PA, Han DH, Marshall BA, Nolte LA, Chen MM, Mueckler M, et al. A high fat diet impairs stimulation of glucose transport in muscle. Functional evaluation of potential mechanisms. J. Biol. Chem. 1998;273(40):26157–26163. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

