Identification and characterization of PNRC splicing variants
- PMID: 18703122
- PMCID: PMC3644619
- DOI: 10.1016/j.gene.2008.07.018
Identification and characterization of PNRC splicing variants
Abstract
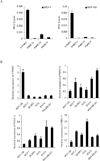
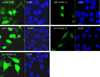
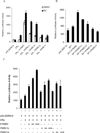
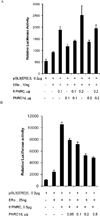
Nuclear receptor (NR) dependent transcriptional action requires recruitment of diverse factors characterized as coregulators. PNRC (proline-rich nuclear receptor coregulatory protein) is a member of coregulators that are capable of potentiating the transcriptional activity of NRs. Here we identified three human PNRC splicing variants designated PNRC1c, PNRC1d and PNRC1f. PNRC1c and PNRC1f are generated through alternative recognition of the 3'-splice site in exon 1, leading to in-frame deletion of 79 amino acids (aa) and an altered reading frame, respectively. PNRC1d is generated through the alternate promoter usage and forms a truncated protein containing C-terminus 142 aa of full-length PNRC. These isoforms differ in their abilities to bind NRs and potentiate NR mediated transcriptions. Moreover, PNRC1d can modulate the activity of full-length PNRC in enhancing ER mediated transcription. Our results suggest that PNRC exists as functionally distinct isoforms and alternative splicing serves as a regulatory mechanism of PNRC coactivator activity.
Figures




Similar articles
-
PNRC: a proline-rich nuclear receptor coregulatory protein that modulates transcriptional activation of multiple nuclear receptors including orphan receptors SF1 (steroidogenic factor 1) and ERRalpha1 (estrogen related receptor alpha-1).Mol Endocrinol. 2000 Jul;14(7):986-98. doi: 10.1210/mend.14.7.0480. Mol Endocrinol. 2000. PMID: 10894149
-
The molecular basis of the interaction between the proline-rich SH3-binding motif of PNRC and estrogen receptor alpha.Nucleic Acids Res. 2006;34(20):5974-86. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkl764. Epub 2006 Oct 26. Nucleic Acids Res. 2006. PMID: 17068076 Free PMC article.
-
[Transcriptional regulation of the human gene coding for proline-rich nuclear receptor coactivator (pnrc) by regulatory factor x (rfx1)].Mol Biol (Mosk). 2009 Jan-Feb;43(1):77-84. Mol Biol (Mosk). 2009. PMID: 19334528 Russian.
-
Regulation of Alternative Splicing by Steroid Hormones.Endocrinology. 2023 Jun 6;164(7):bqad081. doi: 10.1210/endocr/bqad081. Endocrinology. 2023. PMID: 37226268 Review.
-
Splice variants of metabolic nuclear receptors: Relevance for metabolic disease and therapeutic targeting.Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 2021 Oct 1;1867(10):166183. doi: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2021.166183. Epub 2021 May 29. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 2021. PMID: 34058349 Review.
Cited by
-
SGK3 is an estrogen-inducible kinase promoting estrogen-mediated survival of breast cancer cells.Mol Endocrinol. 2011 Jan;25(1):72-82. doi: 10.1210/me.2010-0294. Epub 2010 Nov 17. Mol Endocrinol. 2011. PMID: 21084382 Free PMC article.
-
Function of alternative splicing.Gene. 2013 Feb 1;514(1):1-30. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2012.07.083. Epub 2012 Aug 15. Gene. 2013. PMID: 22909801 Free PMC article. Review.
-
RNA splicing programs define tissue compartments and cell types at single-cell resolution.Elife. 2021 Sep 13;10:e70692. doi: 10.7554/eLife.70692. Elife. 2021. PMID: 34515025 Free PMC article.
-
PNRC accumulates in the nucleolus by interaction with B23/nucleophosmin via its nucleolar localization sequence.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2011 Jan;1813(1):109-19. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2010.09.017. Epub 2010 Oct 1. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2011. PMID: 20888865 Free PMC article.
-
Nuclear receptor coactivators: structural and functional biochemistry.Biochemistry. 2011 Jan 25;50(3):313-28. doi: 10.1021/bi101762x. Epub 2010 Dec 29. Biochemistry. 2011. PMID: 21141906 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Albers M, Kranz H, Kober I, Kaiser C, Klink M, Suckow J, Kern R, Koegl M. Automated yeast two-hybrid screening for nuclear receptor-interacting proteins. Mol Cell Proteomics. 2005;4:205–213. - PubMed
-
- Baek SH, Rosenfeld MG. Nuclear receptor coregulators: their modification codes and regulatory mechanism by translocation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2004;319:707–714. - PubMed
-
- Brinkman BM. Splice variants as cancer biomarkers. Clin Biochem. 2004;37:584–594. - PubMed
-
- Chen J, Liu L, Pohajdak B. Cloning a cDNA from human NK/T cells which codes for a protein with high proline content. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1995;1264:19–22. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

