Intermittent hypoxia has organ-specific effects on oxidative stress
- PMID: 18703411
- PMCID: PMC2576102
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpregu.90346.2008
Intermittent hypoxia has organ-specific effects on oxidative stress
Abstract
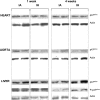
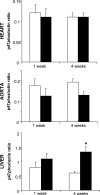
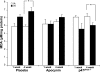
Obstructive sleep apnea is characterized by upper airway collapse, leading to intermittent hypoxia (IH). It has been postulated that IH-induced oxidative stress may contribute to several chronic diseases associated with obstructive sleep apnea. We hypothesize that IH induces systemic oxidative stress by upregulating NADPH oxidase, a superoxide-generating enzyme. NADPH oxidase is regulated by a cytosolic p47(phox) subunit, which becomes phosphorylated during enzyme activation. Male C57BL/6J mice were exposed to IH with an inspired O(2) fraction nadir of 5% 60 times/h during the 12-h light phase (9 AM-9 PM) for 1 or 4 wk. In the aorta and heart, IH did not affect lipid peroxidation [malondialdehyde (MDA) level], nitrotyrosine level, or p47(phox) expression and phosphorylation. In contrast, in the liver, exposure to IH for 1 wk resulted in a trend to an increase in MDA levels, whereas IH for 4 wk resulted in a 38% increase in MDA levels accompanied by upregulation of p47(phox) expression and phosphorylation. Administration of an NADPH oxidase inhibitor, apocynin, during IH exposure attenuated IH-induced increases in hepatic MDA. In p47(phox)-deficient mice, MDA levels were higher at baseline and, unexpectedly, decreased during IH. In conclusion, oxidative stress levels and pathways under IH conditions are organ and duration specific.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Effects of various degrees of oxidative stress induced by intermittent hypoxia in rat myocardial tissues.Respirology. 2012 Jul;17(5):821-9. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1843.2012.02157.x. Respirology. 2012. PMID: 22372715
-
Green tea catechin polyphenols attenuate behavioral and oxidative responses to intermittent hypoxia.Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2008 May 15;177(10):1135-41. doi: 10.1164/rccm.200701-110OC. Epub 2008 Feb 14. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2008. PMID: 18276944 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting NADPH oxidase decreases oxidative stress in the transgenic sickle cell mouse penis.J Sex Med. 2012 Aug;9(8):1980-7. doi: 10.1111/j.1743-6109.2012.02798.x. Epub 2012 May 23. J Sex Med. 2012. PMID: 22620981 Free PMC article.
-
NADPH oxidase in bone marrow-derived cells mediates pulmonary ischemia-reperfusion injury.Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2009 Mar;40(3):375-81. doi: 10.1165/rcmb.2008-0300OC. Epub 2008 Sep 11. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2009. PMID: 18787174 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of intermittent hypoxia on oxidative stress-induced myocardial damage in mice.J Appl Physiol (1985). 2007 May;102(5):1806-14. doi: 10.1152/japplphysiol.01291.2006. Epub 2007 Feb 1. J Appl Physiol (1985). 2007. PMID: 17272404
Cited by
-
The impact of sleep disorders on glucose metabolism: endocrine and molecular mechanisms.Diabetol Metab Syndr. 2015 Mar 24;7:25. doi: 10.1186/s13098-015-0018-3. eCollection 2015. Diabetol Metab Syndr. 2015. PMID: 25834642 Free PMC article.
-
Dim light at night interacts with intermittent hypoxia to alter cognitive and affective responses.Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2013 Jul 1;305(1):R78-86. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.00100.2013. Epub 2013 May 8. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2013. PMID: 23657638 Free PMC article.
-
Vascular effects of intermittent hypoxia.ILAR J. 2009;50(3):282-8. doi: 10.1093/ilar.50.3.282. ILAR J. 2009. PMID: 19506314 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Neonatal Intermittent Hypoxia, Reactive Oxygen Species, and Oxygen-Induced Retinopathy.React Oxyg Species (Apex). 2017 Jan;3(7):12-25. doi: 10.20455/ros.2017.805. React Oxyg Species (Apex). 2017. PMID: 29951586 Free PMC article.
-
Pattern-specific sustained activation of tyrosine hydroxylase by intermittent hypoxia: role of reactive oxygen species-dependent downregulation of protein phosphatase 2A and upregulation of protein kinases.Antioxid Redox Signal. 2009 Aug;11(8):1777-89. doi: 10.1089/ars.2008.2368. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2009. PMID: 19335094 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Acarturk G, Unlu M, Yuksel S, Albayrak R, Koken T, Peker Y. Obstructive sleep apnoea, glucose tolerance and liver steatosis in obese women. J Int Med Res 35: 458–466, 2007. - PubMed
-
- Ambrosio G, Chiariello M. Myocardial reperfusion injury: mechanisms and management—a review. Am J Med 91: 86S–88S, 1991. - PubMed
-
- Ambrus CM, Lajos TZ, Stadler I, Stadler A, Alfano J, Tulumello JA, Ambrus JL Jr. Myocardial release of non-transferrin-bound iron during cardio-pulmonary bypass surgery. J Med 30: 157–167, 1999. - PubMed
-
- Antebi A Ageing: when less is more. Nature 447: 536–537, 2007. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

