Parent based language intervention for 2-year-old children with specific expressive language delay: a randomised controlled trial
- PMID: 18703544
- PMCID: PMC2614563
- DOI: 10.1136/adc.2008.141572
Parent based language intervention for 2-year-old children with specific expressive language delay: a randomised controlled trial
Abstract
Objective: The aim of this randomised controlled trial was to evaluate the effectiveness of a short, highly structured parent based language intervention group programme for 2-year-old children with specific expressive language delay (SELD, without deficits in receptive language).
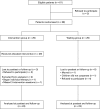
Methods: 61 children with SELD (mean age 24.7 months, SD 0.9) were selected between October 2003 and February 2006 during routine developmental check-ups in general paediatric practices, using a German parent-report screening questionnaire (adapted from the MacArthur Communicative Development Inventories). Standardised instruments were used to assess the language and non-verbal cognitive abilities of these children and of 36 other children with normal language development (reference group; mean age 24.6 months, SD 0.8). 58 children with SELD were sequentially randomly assigned to an intervention group (n = 29) or a 12-month waiting group (n = 29). In the intervention group, mothers participated in the 3-month Heidelberg Parent-based Language Intervention (HPLI). All children were reassessed 6 and 12 months after pretest. Assessors were blind to allocation and previous results.
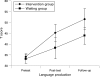
Results: 47 children were included in the analysis. At the age of 3 years, 75% of the children in the intervention group showed normal expressive language abilities in contrast to 44% in the waiting group. Only 8% of the children in the intervention group versus 26% in the waiting group met the criteria for specific language impairment (t score < or =35).
Conclusions: By applying the short, highly structured HPLI in children with SELD, the rate of treatment for language impairment at the age of 3 years can be significantly reduced.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Comment in
-
Wayward words and watchful waiting: should clinicians be more proactive for the preschooler with uncomplicated expressive language delay?Arch Dis Child. 2009 Feb;94(2):80-2. doi: 10.1136/adc.2008.148528. Arch Dis Child. 2009. PMID: 19158135 Review. No abstract available.
-
Parent-based language intervention for 2-year old children with specific expressive language delay: a randomised controlled trial with erroneous confidence (intervals).Arch Dis Child. 2010 Nov;95(11):953. doi: 10.1136/adc.2009.167346. Epub 2010 Sep 29. Arch Dis Child. 2010. PMID: 20880946 No abstract available.
References
-
- Horwitz SM, Irwin JR, Briggs-Gowan M, et al. Language delay in a community cohort of young children. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry 2003;42:932–40 - PubMed
-
- Reilly S, Wake M, Bavin EL, et al. Predicting language at 2 years of age: a prospective community study. Pediatrics 2007;120:1441–9 - PubMed
-
- Buschmann A, Jooss B, Rupp A, et al. Children with developmental language delay at 24 months of age: results of a diagnostic work-up. Dev Med Child Neurol 2008;50:223–9 - PubMed
-
- Paul R. Predicting outcomes of early expressive language delay: ethical implications. Bishop D V M, Leonard L B, eds. Speech and language impairments in children: causes, characteristics, intervention and outcome East Sussex, UK: Psychology Press, 2000:195–209
-
- Deutsche Gesellschaft für Kinder- und Jugendpsychiatrie und Psychotherapie (Hrsg) Leitlinien zur Diagnostik und Therapie von psychischen Störungen im Säuglings-, Kindes- und Jugendalter 3.überarbeitete Auflage.Cologne: Deutscher Ärzte Verlag, 2007:197–206
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous