High dietary inorganic phosphate enhances cap-dependent protein translation, cell-cycle progression, and angiogenesis in the livers of young mice
- PMID: 18703640
- PMCID: PMC2575911
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpgi.90213.2008
High dietary inorganic phosphate enhances cap-dependent protein translation, cell-cycle progression, and angiogenesis in the livers of young mice
Abstract
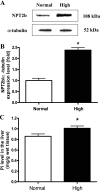
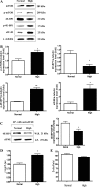
Inorganic phosphate (P(i)) plays a key role in diverse physiological functions. Recent studies have indicated that P(i) affects Akt signaling through the sodium-dependent phosphate cotransporter. Akt signaling, in turn, plays an important role in liver development; however, the effects of high dietary P(i) on the liver have not been investigated. Here, we examined the effects of high dietary phosphate on the liver in developing mice. We found that high dietary P(i) increased liver mass through enhancing Akt-related cap-dependent protein translation, cell cycle progression, and angiogenesis. Thus careful regulation of P(i) consumption may be important in maintaining normal development of the liver.
Figures





References
-
- Asnaghi L, Bruno P, Priulla M, Nicolin A. mTOR: a protein kinase switching between life and death. Pharmacol Res 50: 545–549, 2004. - PubMed
-
- Beck GR Jr, Moran E, Knecht N. Inorganic phosphate regulates multiple genes during osteoblast differentiation, including Nrf2. Exp Cell Res 288: 288–300, 2003. - PubMed
-
- Bremnes RM, Camps C, Sirera R. Angiogenesis in non-small cell lung cancer: the prognostic impact of neoangiogenesis and the cytokines VEGF and bFGF in tumours and blood. Lung Cancer 51: 143–158, 2006. - PubMed
-
- Calvo MS Dietary phosphorus, calcium metabolism, and bone. J Nutr 123: 1627–1633, 1993. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

