A novel three-phase model of brain tissue microstructure
- PMID: 18704170
- PMCID: PMC2495040
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1000152
A novel three-phase model of brain tissue microstructure
Erratum in
- PLoS Comput Biol. 2009 Jan;5(1). doi: 10.1371/annotation/c9faa83b-3c7b-4f38-8d74-1a4309403688
Abstract
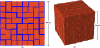
We propose a novel biologically constrained three-phase model of the brain microstructure. Designing a realistic model is tantamount to a packing problem, and for this reason, a number of techniques from the theory of random heterogeneous materials can be brought to bear on this problem. Our analysis strongly suggests that previously developed two-phase models in which cells are packed in the extracellular space are insufficient representations of the brain microstructure. These models either do not preserve realistic geometric and topological features of brain tissue or preserve these properties while overestimating the brain's effective diffusivity, an average measure of the underlying microstructure. In light of the highly connected nature of three-dimensional space, which limits the minimum diffusivity of biologically constrained two-phase models, we explore the previously proposed hypothesis that the extracellular matrix is an important factor that contributes to the diffusivity of brain tissue. Using accurate first-passage-time techniques, we support this hypothesis by showing that the incorporation of the extracellular matrix as the third phase of a biologically constrained model gives the reduction in the diffusion coefficient necessary for the three-phase model to be a valid representation of the brain microstructure.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures


Similar articles
-
A survey of current trends in diffusion MRI for structural brain connectivity.J Neural Eng. 2016 Feb;13(1):011001. doi: 10.1088/1741-2560/13/1/011001. Epub 2015 Dec 22. J Neural Eng. 2016. PMID: 26695367 Review.
-
Factors governing diffusing molecular signals in brain extracellular space.J Neural Transm (Vienna). 2005 Jan;112(1):29-44. doi: 10.1007/s00702-004-0204-1. Epub 2004 Sep 14. J Neural Transm (Vienna). 2005. PMID: 15372328 Review.
-
A model of effective diffusion and tortuosity in the extracellular space of the brain.Biophys J. 2004 Sep;87(3):1606-17. doi: 10.1529/biophysj.103.039495. Biophys J. 2004. PMID: 15345540 Free PMC article.
-
Three-dimensional modeling of the brain's ECS by minimum configurational energy packing of fluid vesicles.Biophys J. 2007 May 15;92(10):3368-78. doi: 10.1529/biophysj.106.095547. Epub 2007 Feb 16. Biophys J. 2007. PMID: 17307830 Free PMC article.
-
Geometric and viscous components of the tortuosity of the extracellular space in the brain.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1998 Jul 21;95(15):8975-80. doi: 10.1073/pnas.95.15.8975. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1998. PMID: 9671789 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Structural Characterization and Statistical-Mechanical Model of Epidermal Patterns.Biophys J. 2016 Dec 6;111(11):2534-2545. doi: 10.1016/j.bpj.2016.10.036. Biophys J. 2016. PMID: 27926854 Free PMC article.
-
Spatial organization and correlations of cell nuclei in brain tumors.PLoS One. 2011;6(11):e27323. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0027323. Epub 2011 Nov 16. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 22110626 Free PMC article.
-
Computational modeling of tumor response to vascular-targeting therapies--part I: validation.Comput Math Methods Med. 2011;2011:830515. doi: 10.1155/2011/830515. Epub 2011 Mar 23. Comput Math Methods Med. 2011. PMID: 21461361 Free PMC article.
-
Dense packings of the Platonic and Archimedean solids.Nature. 2009 Aug 13;460(7257):876-9. doi: 10.1038/nature08239. Nature. 2009. PMID: 19675649
-
Quantitative characterization of the microstructure and transport properties of biopolymer networks.Phys Biol. 2012 Jun;9(3):036009. doi: 10.1088/1478-3975/9/3/036009. Epub 2012 Jun 8. Phys Biol. 2012. PMID: 22683739 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Nicholson C. Diffusion and related transport mechanisms in brain tissue. Rep Prog Phys. 2001;64:815–884.
-
- Syková E, Mazel T, Vargová L, Voříšek I, Prokopová-Kubinová S. Progress in Brain Research: Volume Transmission Revisited. Amsterdam: Elsevier; 2000. Extracellular space diffusion and pathological states. pp. 155–178. Chapter 6. - PubMed
-
- Torquato S. Random Heterogeneous Materials: Microstructure and Macroscopic Properties. New York: Springer-Verlag; 2002.
-
- Nicholson C, Syková E. Extracellular space structure revealed by diffusion analysis. Trends Neurosci. 1998;21:207–215. - PubMed
-
- Sen PN. Diffusion and tissue microstructure. J Phys Condens Matter. 2004;16:S5213–S5220.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

