Differences in innervation and innervated neurons between hip and inguinal skin
- PMID: 18704614
- PMCID: PMC2584300
- DOI: 10.1007/s11999-008-0432-z
Differences in innervation and innervated neurons between hip and inguinal skin
Abstract
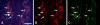
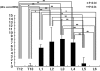
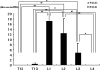
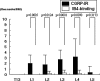
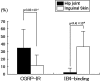
Pain originating from the hip may be referred to the groin and anterior thigh. We investigated sensory dorsal root ganglion neurons innervating the hip and the inguinal skin in rats using retrograde neurotransport and immunohistochemistry. A retrograde neurotracer Fluoro-Gold was injected into the left hip or inguinal skin of rats. Seven days later, we harvested bilateral dorsal root ganglions and counted the number of Fluoro-Gold-labeled neurons positive for calcitonin gene-related peptide, a marker of nerve growth factor-dependent neurons, or isolectin B4, a marker of glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor-dependent neurons. In the hip group, Fluoro-Gold-labeled neurons were distributed throughout the left dorsal root ganglions from T13 to L5, primarily at L1, L2, L3, and L4, and the percentage of calcitonin gene-related peptide-positive neurons was higher than that of isolectin B4-binding neurons. In the inguinal skin group, Fluoro-Gold-labeled neurons were distributed throughout the left dorsal root ganglions from T13 to L3, primarily at L1, L2, and L3, and the percentage of isolectin B4-binding neurons was higher than that of calcitonin gene-related peptide-positive neurons. These data suggest the sensory innervation pattern and characteristics of the sensory nerve of the rat hip are different from those of inguinal skin.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The characteristics of dorsal-root ganglia and sensory innervation of the hip in rats.J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2008 Feb;90(2):254-7. doi: 10.1302/0301-620X.90B2.19808. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2008. PMID: 18256100
-
Innervation of the lumbar intervertebral disc by nerve growth factor-dependent neurons related to inflammatory pain.Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2004 May 15;29(10):1077-81. doi: 10.1097/00007632-200405150-00005. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2004. PMID: 15131432
-
Phenotypic inflammation switch in rats shown by calcitonin gene-related peptide immunoreactive dorsal root ganglion neurons innervating the lumbar facet joints.Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2001 May 1;26(9):1009-13. doi: 10.1097/00007632-200105010-00005. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2001. PMID: 11337618
-
Sensory innervation of the dorsal portion of the lumbar intervertebral discs in rats.Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2001 Apr 15;26(8):946-50. doi: 10.1097/00007632-200104150-00020. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2001. PMID: 11317119
-
Distribution and immunocytochemical characterization of dorsal root ganglion neurons innervating the lumbar intervertebral disc in rats: a review.Life Sci. 2004 Apr 9;74(21):2627-42. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2004.01.008. Life Sci. 2004. PMID: 15041445 Review.
Cited by
-
Anti-nerve growth factor therapy attenuates cutaneous hypersensitivity and musculoskeletal discomfort in mice with osteoporosis.Pain Rep. 2018 Apr 10;3(3):e652. doi: 10.1097/PR9.0000000000000652. eCollection 2018 May. Pain Rep. 2018. PMID: 29922744 Free PMC article.
-
Multisegmental A{delta}- and C-fiber input to neurons in lamina I and the lateral spinal nucleus.J Neurosci. 2010 Feb 10;30(6):2384-95. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3445-09.2010. J Neurosci. 2010. PMID: 20147564 Free PMC article.
-
Dissociation between the relief of skeletal pain behaviors and skin hypersensitivity in a model of bone cancer pain.Pain. 2016 Jun;157(6):1239-1247. doi: 10.1097/j.pain.0000000000000514. Pain. 2016. PMID: 27186713 Free PMC article.
-
A phenotypically restricted set of primary afferent nerve fibers innervate the bone versus skin: therapeutic opportunity for treating skeletal pain.Bone. 2010 Feb;46(2):306-13. doi: 10.1016/j.bone.2009.09.013. Epub 2009 Sep 18. Bone. 2010. PMID: 19766746 Free PMC article.
-
Pain-related sensory innervation in monoiodoacetate-induced osteoarthritis in rat knees that gradually develops neuronal injury in addition to inflammatory pain.BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2011 Jun 16;12:134. doi: 10.1186/1471-2474-12-134. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2011. PMID: 21679434 Free PMC article.
References
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'DOI', 'value': '10.1002/cne.10655', 'is_inner': False, 'url': 'https://doi.org/10.1002/cne.10655'}, {'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '12687682', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/12687682/'}]}
- Ambalavanar R, Moritani M, Haines A, Hilton T, Dessem D. Chemical phenotypes of muscle and cutaneous afferent neurons in the rat trigeminal ganglion. J Comp Neurol. 2003;460:167–179. - PubMed
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'DOI', 'value': '10.1111/j.1460-9568.1995.tb01143.x', 'is_inner': False, 'url': 'https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1460-9568.1995.tb01143.x'}, {'type': 'PMC', 'value': 'PMC2758238', 'is_inner': False, 'url': 'https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC2758238/'}, {'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '7551174', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/7551174/'}]}
- Averill S, McMahon SB, Clary DO, Reichardt LF, Priestley JV. Immunocytochemical localization of trkA receptors in chemically identified subgroups of adult rat sensory neurons. Eur J Neurosci. 1995;7:1484–1494. - PMC - PubMed
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'DOI', 'value': '10.1016/0304-3940(96)12418-6', 'is_inner': False, 'url': 'https://doi.org/10.1016/0304-3940(96)12418-6'}, {'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '8848275', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/8848275/'}]}
- Bennett DL, Dmietrieva N, Priestley JV, Clary D, McMahon SB. trkA, CGRP and IB4 expression in retrogradely labelled cutaneous and visceral primary sensory neurones in the rat. Neurosci Lett. 1996;206:33–36. - PubMed
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'DOI', 'value': '10.1046/j.1460-9568.1998.00139.x', 'is_inner': False, 'url': 'https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1460-9568.1998.00139.x'}, {'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '9749782', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/9749782/'}]}
- Bennett DL, Koltzenburg M, Priestley JV, Shelton DL, McMahon SB. Endogenous nerve growth factor regulates the sensitivity of nociceptors in the adult rat. Eur J Neurosci. 1998;10:1282–1291. - PubMed
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'DOI', 'value': '10.1007/BF01628504', 'is_inner': False, 'url': 'https://doi.org/10.1007/bf01628504'}, {'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '9479711', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/9479711/'}]}
- Birnbaum K, Prescher A, Hessler S, Heller KD. The sensory innervation of the hip joint: an anatomical study. Surg Radiol Anat. 1997;19:371–375. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

