Autologous thrombin: intraoperative production from whole blood
- PMID: 18705544
- PMCID: PMC4680638
Autologous thrombin: intraoperative production from whole blood
Abstract
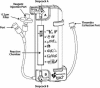
Thrombin is routinely combined in surgical practice with a fibrinogen source to prepare fibrin sealant to promote hemostasis or with platelet concentrates to prepare platelet gels to enhance wound healing. The purpose of this study was to evaluate the robustness and reproducibility of a new sterile handheld disposable thrombin-processing device (TPD) to generate autologous human thrombin in the intraoperative setting, using whole blood as the starting source material. By using whole blood instead of plasma as the starting material, it is possible to eliminate the plasma separation step from whole blood and reduce the thrombin production time and increase its availability to the surgical team intraoperatively. Active thrombin was prepared by combining 4 mL of thrombin reagent (a mixture of calcium chloride and ethanol) to 11 mL of blood in a reaction chamber containing negatively charged particles. The whole blood, reagent and particle mixture was incubated for 25 minutes at either 18 degrees C or 24 degrees C (n = 25/group) to assess stability of the thrombin activity. The mean activity of the thrombin produced at 18 degrees C and 24 degrees C was 52 +/- 14 (n = 25) and 61 +/- 12.2 IU/mL (n = 25), respectively. The average volume of thrombin harvested from each aliquot of blood at 18 degrees C and 24 degrees C was 10 +/- 0.4 and 9 +/- 0.6 mL, respectively. The thrombin concentration generated was shown to rapidly (<5 seconds) coagulate fibrinogen concentrate and retained clotting activity for 1 hour at room temperature (18-26 degrees C) and up to 4 hours when stored on ice. The results show that the TPD is able to consistently generate high thrombin activity from human whole blood. The device offers a robust and rapid approach for preparing active thrombin from whole blood.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have reported a financial relationship with the entity whose products or services are discussed in this paper.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Whole blood thrombin: development of a process for intra-operative production of human thrombin.J Extra Corpor Technol. 2007 Mar;39(1):18-23. J Extra Corpor Technol. 2007. PMID: 17486869 Free PMC article.
-
Stability of human thrombin produced from 11 ml of plasma using the thrombin processing device.J Extra Corpor Technol. 2005 Dec;37(4):390-5. J Extra Corpor Technol. 2005. PMID: 16524159 Free PMC article.
-
Preparation and characterization of human thrombin for use in a fibrin glue.Transfus Med. 2007 Jun;17(3):187-91. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3148.2006.00717.x. Transfus Med. 2007. PMID: 17561860
-
A review of the therapeutic uses of thrombin.Thromb Haemost. 2004 May;91(5):851-60. doi: 10.1160/TH03-12-0792. Thromb Haemost. 2004. PMID: 15116244 Review.
-
Fibrin sealant in orthopedic surgery.Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1988 Feb;227:269-85. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1988. PMID: 2448076 Review.
Cited by
-
A Simple, Safe, and Effective Method for Preparing Autologous Bio-Based Fibrin Glue for Ophthalmic Use.Pharmaceutics. 2022 Oct 28;14(11):2325. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics14112325. Pharmaceutics. 2022. PMID: 36365142 Free PMC article.
-
Beyond 2D: effects of photobiomodulation in 3D tissue-like systems.J Biomed Opt. 2020 Apr;25(4):1-16. doi: 10.1117/1.JBO.25.4.048001. J Biomed Opt. 2020. PMID: 32351077 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Mann KG.. Thrombin formation. Chest. 2003;124(3 Suppl):4S–10S. - PubMed
-
- Aziz O, Athanasiou T, Darzi A.. Haemostasis using a ready-to-use collagen sponge coated with activated thrombin and fibrinogen. Surg Technol Int. 2005;14:35–40. - PubMed
-
- Hashemi K, Donaldson LJ, Freeman JW, Sokhi GS, Gyde OH, Smith HV.. The use of topical thrombin to reduce wound haematoma in patients receiving low-dose heparin. Curr Med Res Opin. 1981;7:458–62. - PubMed
-
- Suzuki R, Matsuhashi M, Kuwahara T, Kase T.. Topical use of thrombin in prostatic surgery. Hinyokika Kiyo. 1986;32:1461–64. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources