Mycobacteria-induced granuloma necrosis depends on IRF-1
- PMID: 18705699
- PMCID: PMC6512360
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1582-4934.2008.00470.x
Mycobacteria-induced granuloma necrosis depends on IRF-1
Abstract
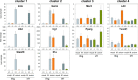
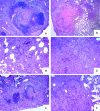
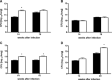
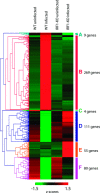
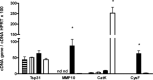
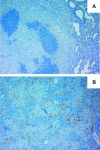
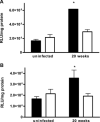
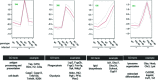
In a mouse model of mycobacteria-induced immunopathology, wild-type C57BL/6 (WT), IL-18-knockout (KO) and IFN-alphabeta receptor-KO mice developed circumscript, centrally necrotizing granulomatous lesions in response to aerosol infection with M. avium, whereas mice deficient in the IFN-gamma receptor, STAT-1 or IRF-1 did not exhibit granuloma necrosis. Comparative, microarray-based gene expression analysis in the lungs of infected WT and IRF-1-KO mice identified a set of genes whose differential regulation was closely associated with granuloma necrosis, among them cathepsin K, cystatin F and matrix metalloprotease 10. Further microarray-based comparison of gene expression in the lungs of infected WT, IFN-gamma-KO and IRF-1-KO mice revealed four distinct clusters of genes with variable dependence on the presence of IFN-gamma, IRF-1 or both. In particular, IRF-1 appeared to be directly involved in the differentiation of a type I immune response to mycobacterial infection. In summary, IRF-1, rather than being a mere transcription factor downstream of IFN-gamma, may be a master regulator of mycobacteria-induced immunopathology.
Figures
References
-
- Ehlers S, Hölscher C. DTH‐associated pathology. In: Kaufmann SH, Steward MW, editors. Topley & Wilson’s microbiology and microbial infections: immunology. London : Hodder Arnold; 2005. pp. 705–29.
-
- Dheda K, Booth H, Huggett JF, et al . Lung remodeling in pulmonary tuberculosis. J Infect Dis . 2005; 192: 1201–9. - PubMed
-
- North RJ, Jung YJ. Immunity to tuberculosis. Annu Rev Immunol . 2004; 22: 599–623. - PubMed
-
- Benini J, Ehlers EM, Ehlers S. Different types of pulmonary granuloma necrosis in immunocompetent vs. TNFRp55‐gene‐deficient mice aerogenically infected with highly virulent Mycobacterium avium. J Pathol . 1999; 189: 127–37. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

