HrpN of Erwinia amylovora functions in the translocation of DspA/E into plant cells
- PMID: 18705858
- PMCID: PMC6640523
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1364-3703.2008.00471.x
HrpN of Erwinia amylovora functions in the translocation of DspA/E into plant cells
Abstract
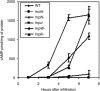
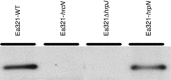
The type III secretion system (T3SS) is required by plant pathogenic bacteria for the translocation of certain bacterial proteins to the cytoplasm of plant cells or secretion of some proteins to the apoplast. The T3SS of Erwinia amylovora, which causes fire blight of pear, apple and other rosaceous plants, secretes DspA/E, which is an indispensable pathogenicity factor. Several other proteins, including HrpN, a critical virulence factor, are also secreted by the T3SS. Using a CyaA reporter system, we demonstrated that DspA/E is translocated into the cells of Nicotiana tabacum'Xanthi'. To determine if other T3-secreted proteins are needed for translocation of DspA/E, we examined its translocation in several mutants of E. amylovora strain Ea321. DspA/E was translocated by both hrpW and hrpK mutants, although with some delay, indicating that these two proteins are dispensable in the translocation of DspA/E. Remarkably, translocation of DspA/E was essentially abolished in both hrpN and hrpJ mutants; however, secretion of DspA/E into medium was not affected in any of the mentioned mutants. In contrast to the more virulent strain Ea273, secretion of HrpN was abolished in a hrpJ mutant of strain Ea321. In addition, HrpN was weakly translocated into plant cytoplasm. These results suggest that HrpN plays a significant role in the translocation of DspA/E, and HrpJ affects the translocation of DspA/E by affecting secretion or stability of HrpN. Taken together, these results explain the critical importance of HrpN and HrpJ to the development of fire blight.
Figures



References
-
- Alfano, J.R. and Collmer, A. (2004) Type III secretion system effector proteins: double agents in bacterial disease and plant defense. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 42, 385–414. - PubMed
-
- Barny, M.A. (1995) Erwinia‐amylovora HrpN mutants, blocked in harpin synthesis, express a reduced virulence on host plants and elicit variable hypersensitive reactions on tobacco. Eur. J. Plant Pathol. 101, 333–340.
-
- Bell, K.S. , Sebaihia, M. , Pritchard, L. , Holden, M.T.G. , Hyman, L.J. , Holeva, M.C. , Thomson, N.R. , Bentley, S.D. , Churcher, L.J.C. , Mungall, K. , Atkin, R. , Bason, N. , Brooks, K. , Chillingworth, T. , Clark, K. , Doggett, J. , Fraser, A. , Hance, Z. , Hauser, H. , Jagels, K. , Moule, S. , Norbertczak, H. , Ormond, D. , Price, C. , Quail, M.A. , Sanders, M. , Walker, D. , Whitehead, S. , Salmond, G.P.C. , Birch, P.R.J. , Parkhill, J. and Toth, I.K. (2004) Genome sequence of the enterobacterial phytopathogen Erwinia carotovora subsp. atroseptica and characterization of virulence factors. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA, 101, 11105–11110. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

