Proteomic analysis identifies MMP-9, DJ-1 and A1BG as overexpressed proteins in pancreatic juice from pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma patients
- PMID: 18706098
- PMCID: PMC2528014
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2407-8-241
Proteomic analysis identifies MMP-9, DJ-1 and A1BG as overexpressed proteins in pancreatic juice from pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma patients
Abstract
Background: There is an urgent need to discover more sensitive and specific biomarkers to improve early diagnosis and screen high-risk patients for pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC). Pancreatic juice is an ideal specimen for PDAC biomarkers discovery, because it is an exceptionally rich source of proteins released from pancreatic cancer cells.
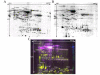
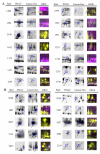
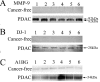
Methods: To identify novel potential biomarkers for PDAC from pancreatic juice, we carried out difference gel electrophoresis (DIGE) and tandem mass spectrometry (MS/MS) to compare the pancreatic juice profiling from 9 PDAC patients and 9 cancer-free controls. Of the identified differently expressed proteins, three up-regulated proteins in pancreatic cancer juice, matrix metalloproteinase-9 (MMP-9), oncogene DJ1 (DJ-1) and alpha-1B-glycoprotein precursor (A1BG), were selected for validation by Western blot and immunohistochemistry. Serum MMP-9 levels were also detected by enzyme linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA).
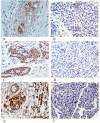
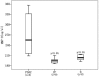
Results: Fourteen proteins were up-regulated and ten proteins were down-regulated in cancerous pancreatic juice compared with cancer-free controls. Increased MMP-9, DJ-1 and A1BG expression in cancerous pancreatic juice were confirmed by Western blot. Immunohistochemical study showed MMP-9, DJ-1 and A1BG positively expressed in 82.4%, 72.5% and 86.3% of pancreatic cancer tissues, significantly higher than that in normal pancreas tissues. Up-regulation of DJ-1 was associated with better differentiation (p < 0.05). Serum MMP-9 levels were significantly higher in PDAC (255.14 ng/ml) than those in chronic pancreatitis (210.22 ng/ml, p = 0.009) and healthy control (203.77 ng/ml, p = 0.027).
Conclusion: The present proteome analysis revealed MMP-9, DJ-1 and A1BG proteins as elevated in pancreatic juice from PDAC, which suggest their further utility in PDAC diagnosis and screening. This is the first time A1BG was identified as a potential biomarker in pancreatic cancer associated samples. The measurement of serum MMP-9 might be clinically useful for PDAC diagnosis.
Figures
References
-
- Steinberg W. The clinical utility of the CA 19-9 tumor-associated antigen. The American journal of gastroenterology. 1990;85:350–355. - PubMed
-
- Rosty C, Christa L, Kuzdzal S, Baldwin WM, Zahurak ML, Carnot F, Chan DW, Canto M, Lillemoe KD, Cameron JL, Yeo CJ, Hruban RH, Goggins M. Identification of hepatocarcinoma-intestine-pancreas/pancreatitis-associated protein I as a biomarker for pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma by protein biochip technology. Cancer research. 2002;62:1868–1875. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

