Expression and localization of the novel and highly conserved gametocyte-specific factor 1 during oogenesis and spermatogenesis
- PMID: 18706558
- PMCID: PMC4852867
- DOI: 10.1016/j.fertnstert.2008.05.042
Expression and localization of the novel and highly conserved gametocyte-specific factor 1 during oogenesis and spermatogenesis
Abstract
Objective: To determine the onset of gametocyte-specific factor 1 (Gtsf1) expression in embryogenesis and its relation to Nobox; and to determine its localization during gonadal development and gametocyte maturation.
Design: Developmental animal study.
Setting: University reproductive biology laboratory.
Animal(s): Mice ranging in age from embryonic day 12.5 to 8 weeks.
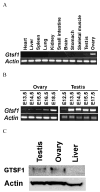
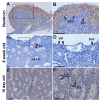
Intervention(s): Polymerase chain reaction and quantitative polymerase chain reaction were performed to determine the onset of and relative messenger RNA expression. Western blot was performed to confirm protein expression and antibody specificity. In situ hybridization and immunohistochemistry were used determine localization of expression.
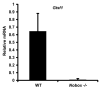
Main outcome measure(s): Gtsf1 messenger RNA expression levels during embryogenesis through adulthood in wild-type mice and in newborn Nobox knockout mice; GTSF1 expression and localization in postnatal mice.
Result(s): Gtsf1 functions downstream of Nobox and is highly expressed in embryonic male and female gonads, localizing to germ cells throughout development. GTSF1 expression is confined to the cytoplasm in all stages of postnatal oocyte maturation and to prespermatogonia during early postnatal testicular development.
Conclusion(s): The expression pattern of Gtsf1 and its high conservation suggests that it may play an important role in germ cell development. Further characterization of Gtsf1 may elucidate mechanisms involved in premature ovarian failure.
Conflict of interest statement
None of the above authors has any potential conflict of interest, financial or otherwise.
Figures
References
-
- Lawson KA, Hage WJ. Clonal analysis of the origin of primordial germ cells in the mouse. Ciba Found Symp. 1994;182:68–84. discussion 84–91. - PubMed
-
- McClellan KA, Gosden R, Taketo T. Continuous loss of oocytes throughout meiotic prophase in the normal mouse ovary. Dev Biol. 2003;258:334–348. - PubMed
-
- Elvin JA, Yan C, Matzuk MM. Oocyte-expressed TGF-beta superfamily members in female fertility. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2000;159:1–5. - PubMed
-
- Pepling ME, Spradling AC. Mouse ovarian germ cell cysts undergo programmed breakdown to form primordial follicles. Dev Biol. 2001;234:339–51. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

