A SARS-CoV protein, ORF-6, induces caspase-3 mediated, ER stress and JNK-dependent apoptosis
- PMID: 18708124
- PMCID: PMC7115782
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbagen.2008.07.009
A SARS-CoV protein, ORF-6, induces caspase-3 mediated, ER stress and JNK-dependent apoptosis
Abstract
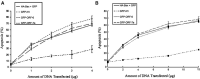
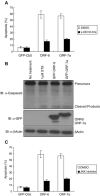
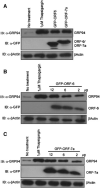
Severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS) coronavirus (CoV) spread from China to more than 30 countries, causing severe outbreaks of atypical pneumonia and over 800 deaths worldwide. CoV primarily infects the upper respiratory and gastrointestinal tract; however, SARS-CoV has a unique pathogenesis because it infects both the upper and lower respiratory tracts and leads to human respiratory diseases. SARS-CoV genome has shown containing 14 open reading frames (ORFs) and 8 of them encode novel proteins. Previous reports show that overexpression of ORF-3a, ORF-3b and ORF-7a induce apoptosis. In this report, we demonstrate that overexpression of ORF-6 also induces apoptosis and that Caspase-3 inhibitor and JNK inhibitor block ORF-6 induced apoptosis. Importantly, the protein level of ER chaperon protein, GRP94, was up-regulated when ORF-6 was overexpressed. All these data suggest that ORF-6 induces apoptosis via Caspase-3 mediated, ER stress and JNK-dependent pathways.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Lead induces the expression of endoplasmic reticulum chaperones GRP78 and GRP94 in vascular endothelial cells via the JNK-AP-1 pathway.Toxicol Sci. 2010 Apr;114(2):378-86. doi: 10.1093/toxsci/kfq008. Epub 2010 Jan 13. Toxicol Sci. 2010. PMID: 20071421
-
Overexpression of 7a, a protein specifically encoded by the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus, induces apoptosis via a caspase-dependent pathway.J Virol. 2004 Dec;78(24):14043-7. doi: 10.1128/JVI.78.24.14043-14047.2004. J Virol. 2004. PMID: 15564512 Free PMC article.
-
Arsenic induces reactive oxygen species-caused neuronal cell apoptosis through JNK/ERK-mediated mitochondria-dependent and GRP 78/CHOP-regulated pathways.Toxicol Lett. 2014 Jan 3;224(1):130-40. doi: 10.1016/j.toxlet.2013.10.013. Epub 2013 Oct 21. Toxicol Lett. 2014. PMID: 24157283
-
Overexpression of endoplasmic reticulum-resident chaperone attenuates cardiomyocyte death induced by proteasome inhibition.Cardiovasc Res. 2008 Sep 1;79(4):600-10. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvn128. Epub 2008 May 28. Cardiovasc Res. 2008. PMID: 18508854
-
[Basic information of Coronavirus].Uirusu. 2020;70(1):29-36. doi: 10.2222/jsv.70.29. Uirusu. 2020. PMID: 33967109 Review. Japanese.
Cited by
-
The SARS-Coronavirus Infection Cycle: A Survey of Viral Membrane Proteins, Their Functional Interactions and Pathogenesis.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Jan 28;22(3):1308. doi: 10.3390/ijms22031308. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33525632 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Coronaviruses: Innate Immunity, Inflammasome Activation, Inflammatory Cell Death, and Cytokines.Trends Immunol. 2020 Dec;41(12):1083-1099. doi: 10.1016/j.it.2020.10.005. Epub 2020 Oct 15. Trends Immunol. 2020. PMID: 33153908 Free PMC article. Review.
-
SARS-CoV-2-Encoded Proteome and Human Genetics: From Interaction-Based to Ribosomal Biology Impact on Disease and Risk Processes.J Proteome Res. 2020 Nov 6;19(11):4275-4290. doi: 10.1021/acs.jproteome.0c00421. Epub 2020 Aug 10. J Proteome Res. 2020. PMID: 32686937 Free PMC article. Review.
-
SARS-CoV-2 and other coronaviruses negatively influence mitochondrial quality control: beneficial effects of melatonin.Pharmacol Ther. 2021 Aug;224:107825. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2021.107825. Epub 2021 Mar 1. Pharmacol Ther. 2021. PMID: 33662449 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus replication is severely impaired by MG132 due to proteasome-independent inhibition of M-calpain.J Virol. 2012 Sep;86(18):10112-22. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01001-12. Epub 2012 Jul 11. J Virol. 2012. PMID: 22787216 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Drosten C., Gunther S., Preiser W., van der Werf S., Brodt H.R., Becker S., Rabenau H., Panning M., Kolesnikova L., Fouchier R.A., Berger A., Burguiere A.M., Cinatl J., Eickmann M., Escriou N., Grywna K., Kramme S., Manuguerra J.C., Muller S., Rickerts V., Sturmer M., Vieth S., Klenk H.D., Osterhaus A.D., Schmitz H., Doerr H.W. Identification of a novel coronavirus in patients with severe acute respiratory syndrome. N. Engl. J. Med. 2003;348:1967–1976. - PubMed
-
- Ksiazek T.G., Erdman D., Goldsmith C.S., Zaki S.R., Peret T., Emery S., Tong S., Urbani C., Comer J.A., Lim W., Rollin P.E., Dowell S.F., Ling A.E., Humphrey C.D., Shieh W.J., Guarner J., Paddock C.D., Rota P., Fields B., DeRisi J., Yang J.Y., Cox N., Hughes J.M., LeDuc J.W., Bellini W.J., Anderson L.J. A novel coronavirus associated with severe acute respiratory syndrome. N. Engl. J. Med. 2003;348:1953–1966. - PubMed
-
- Lee N., Hui D., Wu A., Chan P., Cameron P., Joynt G.M., Ahuja A., Yung M.Y., Leung C.B., To K.F., Lui S.F., Szeto C.C., Chung S., Sung J.J. A major outbreak of severe acute respiratory syndrome in Hong Kong. N. Engl. J. Med. 2003;348:1986–1994. - PubMed
-
- Marra M.A., Jones S.J., Astell C.R., Holt R.A., Brooks-Wilson A., Butterfield Y.S., Khattra J., Asano J.K., Barber S.A., Chan S.Y., Cloutier A., Coughlin S.M., Freeman D., Girn N., Griffith O.L., Leach S.R., Mayo M., McDonald H., Montgomery S.B., Pandoh P.K., Petrescu A.S., Robertson A.G., Schein J.E., Siddiqui A., Smailus D.E., Stott J.M., Yang G.S., Plummer F., Andonov A., Artsob H., Bastien N., Bernard K., Booth T.F., Bowness D., Czub M., Drebot M., Fernando L., Flick R., Garbutt M., Gray M., Grolla A., Jones S., Feldmann H., Meyers A., Kabani A., Li Y., Normand S., Stroher U., Tipples G.A., Tyler S., Vogrig R., Ward D., Watson B., Brunham R.C., Krajden M., Petric M., Skowronski D.M., Upton C., Roper R.L. The genome sequence of the SARS-associated coronavirus. Science. 2003;300:1399–1404. (New York, N.Y.) - PubMed
-
- Peiris J.S., Chu C.M., Cheng V.C., Chan K.S., Hung I.F., Poon L.L., Law K.I., Tang B.S., Hon T.Y., Chan C.S., Chan K.H., Ng J.S., Zheng B.J., Ng W.L., Lai R.W., Guan Y., Yuen K.Y. Clinical progression and viral load in a community outbreak of coronavirus-associated SARS pneumonia: a prospective study. Lancet. 2003;361:1767–1772. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

