TOR signaling is required for amino acid stimulation of early trypsin protein synthesis in the midgut of Aedes aegypti mosquitoes
- PMID: 18708143
- PMCID: PMC2570706
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ibmb.2008.07.003
TOR signaling is required for amino acid stimulation of early trypsin protein synthesis in the midgut of Aedes aegypti mosquitoes
Abstract
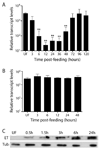
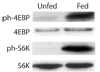
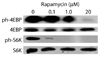
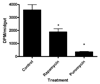
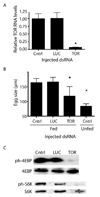
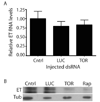
Blood meal digestion in mosquitoes occurs in two phases, an early phase that is translationally regulated, and a late phase that is transcriptionally regulated. Early trypsin is a well-characterized serine endoprotease that is representative of other early phase proteases in the midgut that are only synthesized after feeding. Since the kinase Target of Rapamycin (TOR) has been implicated as a nutrient sensor in other systems, including the mosquito fat body, we tested if TOR signaling is involved in early trypsin protein synthesis in the mosquito midgut in response to feeding. We found that ingestion of an amino acid meal by female mosquitoes induces early trypsin protein synthesis, coincident with phosphorylation of two known TOR target proteins, p70S6 kinase (S6K) and the translational repressor 4E-Binding Protein (4E-BP). Moreover, in vitro culturing of midguts from unfed mosquitoes led to amino acid-dependent phosphorylation of S6K and 4E-BP which could be blocked by treatment with rapamycin, a TOR-specific inhibitor. Lastly, by injecting mosquitoes with TOR double stranded RNA (dsRNA) or rapamycin, we demonstrated that TOR signaling was required in vivo for both phosphorylation of S6K and 4E-BP in the midgut, and for translation of early trypsin mRNA in response to amino acid feeding. It may be possible to target the TOR signaling pathway in the midgut to inhibit blood meal digestion, and thereby, decrease fecundity and the spread of mosquito borne diseases.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Insulin-like peptides and the target of rapamycin pathway coordinately regulate blood digestion and egg maturation in the mosquito Aedes aegypti.PLoS One. 2011;6(5):e20401. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0020401. Epub 2011 May 27. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 21647424 Free PMC article.
-
Nutritional and hormonal regulation of the TOR effector 4E-binding protein (4E-BP) in the mosquito Aedes aegypti.FASEB J. 2012 Mar;26(3):1334-42. doi: 10.1096/fj.11-189969. Epub 2011 Dec 9. FASEB J. 2012. PMID: 22159149 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular genetic analysis of midgut serine proteases in Aedes aegypti mosquitoes.Insect Biochem Mol Biol. 2009 Dec;39(12):903-12. doi: 10.1016/j.ibmb.2009.10.008. Epub 2009 Nov 3. Insect Biochem Mol Biol. 2009. PMID: 19883761 Free PMC article.
-
Target of rapamycin-dependent activation of S6 kinase is a central step in the transduction of nutritional signals during egg development in a mosquito.J Biol Chem. 2005 May 27;280(21):20565-72. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M500712200. Epub 2005 Mar 23. J Biol Chem. 2005. PMID: 15788394
-
Growth control via TOR kinase signaling, an intracellular sensor of amino acid and energy availability, with crosstalk potential to proline metabolism.Amino Acids. 2008 Nov;35(4):761-70. doi: 10.1007/s00726-008-0100-3. Epub 2008 Jul 24. Amino Acids. 2008. PMID: 18651095 Review.
Cited by
-
COPI-mediated blood meal digestion in vector mosquitoes is independent of midgut ARF-GEF and ARF-GAP regulatory activities.Insect Biochem Mol Biol. 2013 Aug;43(8):732-9. doi: 10.1016/j.ibmb.2013.05.005. Epub 2013 May 30. Insect Biochem Mol Biol. 2013. PMID: 23727611 Free PMC article.
-
Expression of active trypsin-like serine peptidases in the midgut of sugar-feeding female Anopheles aquasalis.Parasit Vectors. 2015 May 29;8:296. doi: 10.1186/s13071-015-0908-0. Parasit Vectors. 2015. PMID: 26021986 Free PMC article.
-
Tyrosine transfer RNA levels and modifications during blood-feeding and vitellogenesis in the mosquito, Aedes aegypti.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2023 Nov 29:2023.11.29.569187. doi: 10.1101/2023.11.29.569187. bioRxiv. 2023. Update in: Insect Mol Biol. 2025 Feb;34(1):65-80. doi: 10.1111/imb.12950. PMID: 38076852 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Non-canonical transcriptional regulation of heme oxygenase in Aedes aegypti.Sci Rep. 2019 Sep 24;9(1):13726. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-49396-3. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 31551499 Free PMC article.
-
A Culex quinquefasciatus strain resistant to the binary toxin from Lysinibacillus sphaericus displays altered enzyme activities and energy reserves.Parasit Vectors. 2023 Aug 9;16(1):273. doi: 10.1186/s13071-023-05893-z. Parasit Vectors. 2023. PMID: 37559134 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Arsham AM, Neufeld TP. Thinking globally and acting locally with TOR. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2006;18:589–597. - PubMed
-
- Attardo GM, Hansen IA, Shiao SH, Raikhel AS. Identification of two cationic amino acid transporters required for nutritional signaling during mosquito reproduction. J Exp Biol. 2006;209:3071–3078. - PubMed
-
- Averous J, Proud CG. When translation meets transformation: the mTOR story. Oncogene. 2006;25:6423–6435. - PubMed
-
- Backer JM. The regulation and function of Class III PI3Ks: novel roles for Vps34. Biochem J. 2008;410:1–17. - PubMed
-
- Briegel H. Physiological bases of mosquito ecology. J Vector Ecol. 2003;28:1–11. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

