Deletion of lysophosphatidic acid receptor LPA1 reduces neurogenesis in the mouse dentate gyrus
- PMID: 18708146
- PMCID: PMC3667670
- DOI: 10.1016/j.mcn.2008.07.014
Deletion of lysophosphatidic acid receptor LPA1 reduces neurogenesis in the mouse dentate gyrus
Abstract
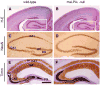
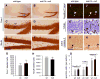
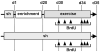
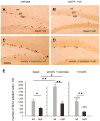
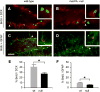
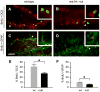
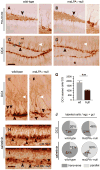
Neurogenesis persists in certain regions of the adult brain including the subgranular zone of the hippocampal dentate gyrus wherein its regulation is essential, particularly in relation to learning, stress and modulation of mood. Lysophosphatidic acid (LPA) is an extracellular signaling phospholipid with important neural regulatory properties mediated by specific G protein-coupled receptors, LPA(1-5). LPA(1) is highly expressed in the developing neurogenic ventricular zone wherein it is required for normal embryonic neurogenesis, and, by extension may play a role in adult neurogenesis as well. By means of the analyses of a variant of the original LPA(1)-null mutant mouse, termed the Malaga variant or "maLPA(1)-null," which has recently been reported to have defective neurogenesis within the embryonic cerebral cortex, we report here a role for LPA(1) in adult hippocampal neurogenesis. Proliferation, differentiation and survival of newly formed neurons are defective in the absence of LPA(1) under normal conditions and following exposure to enriched environment and voluntary exercise. Furthermore, analysis of trophic factors in maLPA(1)-null mice demonstrated alterations in brain-derived neurotrophic factor and insulin growth factor 1 levels after enrichment and exercise. Morphological analyses of doublecortin positive cells revealed the anomalous prevalence of bipolar cells in the subgranular zone, supporting the operation of LPA(1) signaling pathways in normal proliferation, maturation and differentiation of neuronal precursors.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Absence of LPA1 signaling results in defective cortical development.Cereb Cortex. 2008 Apr;18(4):938-50. doi: 10.1093/cercor/bhm132. Epub 2007 Jul 26. Cereb Cortex. 2008. PMID: 17656621
-
Aggravation of chronic stress effects on hippocampal neurogenesis and spatial memory in LPA₁ receptor knockout mice.PLoS One. 2011;6(9):e25522. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0025522. Epub 2011 Sep 29. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 21980482 Free PMC article.
-
Chronic central modulation of LPA/LPA receptors-signaling pathway in the mouse brain regulates cognition, emotion, and hippocampal neurogenesis.Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 2021 Jun 8;108:110156. doi: 10.1016/j.pnpbp.2020.110156. Epub 2020 Nov 2. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 2021. PMID: 33152386
-
Review: adult neurogenesis contributes to hippocampal plasticity.Cell Tissue Res. 2018 Sep;373(3):693-709. doi: 10.1007/s00441-017-2735-4. Epub 2017 Nov 29. Cell Tissue Res. 2018. PMID: 29185071 Review.
-
Genetics and cell biology of lysophosphatidic acid receptor-mediated signaling during cortical neurogenesis.J Cell Biochem. 2004 Aug 1;92(5):1004-12. doi: 10.1002/jcb.20061. J Cell Biochem. 2004. PMID: 15258921 Review.
Cited by
-
maLPA1-null mice as an endophenotype of anxious depression.Transl Psychiatry. 2017 Apr 4;7(4):e1077. doi: 10.1038/tp.2017.24. Transl Psychiatry. 2017. PMID: 28375206 Free PMC article.
-
G-protein-coupled receptors in adult neurogenesis.Pharmacol Rev. 2012 Jul;64(3):645-75. doi: 10.1124/pr.111.004762. Epub 2012 May 18. Pharmacol Rev. 2012. PMID: 22611178 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Lysophosphatidic Acid (LPA) and Its Receptors in Mood Regulation: A Systematic Review of the Molecular Mechanisms and Therapeutic Potential.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jul 6;25(13):7440. doi: 10.3390/ijms25137440. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39000547 Free PMC article.
-
Potential association of plasma lysophosphatidic acid (LPA) species with cognitive impairment in abstinent alcohol use disorders outpatients.Sci Rep. 2020 Oct 13;10(1):17163. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-74155-0. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 33051508 Free PMC article.
-
Lysophospholipid receptors in neurodegeneration and neuroprotection.Explor Neuroprotective Ther. 2024;4(4):349-365. doi: 10.37349/ent.2024.00088. Epub 2024 Aug 22. Explor Neuroprotective Ther. 2024. PMID: 39247084 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Åberg MAI, Åberg ND, Palmer TD, Alborn A, Carlsson-Skwirut C, Bang P, Rosengren LE, Olsson T, Gage FH, Eriksson PS. IGF-I has a direct proliferative effect in adult hippocampal progenitor cells. Mol Cell Neurosci. 2003;24:2–40. - PubMed
-
- Abrous DN, Koehl M, Le Moal M. Adult neurogenesis: from precursors to network and physiology. Physiol Rev. 2005;85:523–569. - PubMed
-
- Ahn S, Joyner AL. In vivo analysis of quiescent adult neural stem cells responding to Sonic hedgehog. Nature. 2005;437:894–897. - PubMed
-
- Aimone JB, Wiles J, Gage FH. Potential role for adult neurogenesis in the encoding of time in new memories. Nat Neurosci. 2006;9:723–727. - PubMed
-
- Allard J, Barrón S, Diaz J, Lubetzki C, Zalc B, Schwartz JC, Sokoloff P. A rat G protein-coupled receptor selectively expressed in myelin-forming cells. E J Neurosci. 1998;10:1045–1053. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

