Prognostic factors and outcomes in patients with leptomeningeal melanomatosis
- PMID: 18708343
- PMCID: PMC2718998
- DOI: 10.1215/15228517-2008-062
Prognostic factors and outcomes in patients with leptomeningeal melanomatosis
Abstract
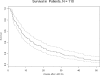
The purpose of this study was to describe a cohort of patients with leptomeningeal melanomatosis (LM) and to determine prognostic factors for outcomes in these patients. The primary hypothesis was that more extensive burden of CNS metastasis at the time of diagnosis of LM (as evidenced by imaging of the CNS parenchyma and meninges and cerebrospinal fluid [CSF] cytology status [positive versus negative]) correlates with poorer outcomes. The records of all patients with LM treated at M. D. Anderson Cancer Center between 1944 and 2002 were reviewed. Information on clinical course and outcomes was gathered. Univariate and multivariate analyses were performed on 110 patients using Cox proportional hazards regression analysis to examine the effects of possible predictive factors on survival. The overall median survival from LM diagnosis was 10 weeks, with a 95% confidence interval (CI) of 8-14 weeks. Eighty-six (78.2%) patients had cutaneous primary lesions, and 23 (20.9%) had melanoma of unknown primary site. The primary hypothesis was not proven. Neither the presence of parenchymal CNS metastases, nor greater imaging evidence of LM, nor positive CSF cytology at diagnosis correlated with survival outcomes. Univariate analyses revealed possible predictors of longer survival, including the presence of supratentorial or spinal LM on imaging at diagnosis versus its absence and any treatment of LM, whereas elevated serum lactate dehydrogenase at the time of LM diagnosis predicted shorter survival. Multivariate analysis revealed that a history of a primary melanoma lesion originating on the trunk predicted shorter survival after LM diagnosis (hazard ratio [HR] = 2.0, 95% CI = 1.0-3.8, p = 0.035), and treatment with intrathecal chemotherapy predicted longer survival (HR = 0.5, 95% CI = 0.4-0.8, p = 0.0036). The positive result with respect to treatment is unreliable due to the inability to remove treatment selection bias from the analysis. This retrospective analysis confirmed the dismal prognosis associated with LM. The amount of CNS tumor burden at the time of diagnosis of LM did not inversely correlate with survival outcomes, contrary to our hypothesis.
Figures
References
-
- Groves MD. Leptomeningeal carcinomatosis: diagnosis and management. In: Sawaya R, editor. Intracranial Metastases: Current Management Strategies. Malden, MA: BlackwellFutura; 2004. pp. 309–330.
-
- Balm M, Hammack J. Leptomeningeal carcinomatosis: presenting features and prognostic factors. Arch Neurol. 1996;53:626–632. - PubMed
-
- Yap HY, Yap BS, Rasmussen S, et al. Treatment for meningeal carcinomatosis in breast cancer. Cancer. 1982;15:219–222. - PubMed
-
- Rosen ST, Aisner J, Makuch RW, et al. Carcinomatous leptomeningitis in small cell lung cancer: a clinicopathologic review for the National Cancer Institute experience. Medicine (Baltimore) 1982;61:45–53. - PubMed
-
- Amer MH, Al-Sarraf M, Baker LH, et al. Malignant melanoma and central nervous system metastasis: incidence, diagnosis, treatment, and survival. Cancer. 1978;42:660–668. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical