RD19, an Arabidopsis cysteine protease required for RRS1-R-mediated resistance, is relocalized to the nucleus by the Ralstonia solanacearum PopP2 effector
- PMID: 18708476
- PMCID: PMC2553607
- DOI: 10.1105/tpc.108.058685
RD19, an Arabidopsis cysteine protease required for RRS1-R-mediated resistance, is relocalized to the nucleus by the Ralstonia solanacearum PopP2 effector
Erratum in
-
CORRECTION.Plant Cell. 2020 Sep;32(9):3036-3037. doi: 10.1105/tpc.20.00482. Epub 2020 Jul 2. Plant Cell. 2020. PMID: 32616660 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
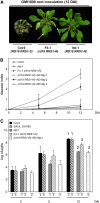
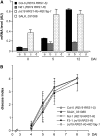
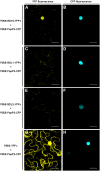
Bacterial wilt, a disease impacting cultivated crops worldwide, is caused by the pathogenic bacterium Ralstonia solanacearum. PopP2 (for Pseudomonas outer protein P2) is an R. solanacearum type III effector that belongs to the YopJ/AvrRxv protein family and interacts with the Arabidopsis thaliana RESISTANT TO RALSTONIA SOLANACEARUM 1-R (RRS1-R) resistance protein. RRS1-R contains the Toll/Interleukin1 receptor-nucleotide binding site-Leu-rich repeat domains found in several cytoplasmic R proteins and a C-terminal WRKY DNA binding domain. In this study, we identified the Arabidopsis Cys protease RESPONSIVE TO DEHYDRATION19 (RD19) as being a PopP2-interacting protein whose expression is induced during infection by R. solanacearum. An Arabidopsis rd19 mutant in an RRS1-R genetic background is compromised in resistance to the bacterium, indicating that RD19 is required for RRS1-R-mediated resistance. RD19 normally localizes in mobile vacuole-associated compartments and, upon coexpression with PopP2, is specifically relocalized to the plant nucleus, where the two proteins physically interact. No direct physical interaction between RRS1-R and RD19 in the presence of PopP2 was detected in the nucleus as determined by Förster resonance energy transfer. We propose that RD19 associates with PopP2 to form a nuclear complex that is required for activation of the RRS1-R-mediated resistance response.
Figures
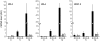

References
-
- Axtell, M.J., and Staskawicz, B.J. (2003). Initiation of RPS2-specified disease resistance in Arabidopsis is coupled to the AvrRpt2-directed elimination of RIN4. Cell 112 369–377. - PubMed
-
- Barrett, A.J., and Rawlings, N.D. (2001). Evolutionary lines of Cysteine peptidases. Biol. Chem. 382 727–733. - PubMed
-
- Belkhadir, Y., Nimchuk, Z., Hubert, D.A., Mackey, D., and Dangl, J.L. (2004). Arabidopsis RIN4 negatively regulates disease resistance mediated by RPS2 and RPM1 downstream or independent of the NDR1 signal modulator and is not required for the virulence functions of bacterial type III effectors AvrRpt2 or AvrRpm1. Plant Cell 16 2822–2835. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Biener, E., Charlier, M., Ramanujan, V.K., Daniel, N., Eisenberg, A., Bjorbaek, C., Herman, B., Gertler, A., and Djiane, J. (2005). Quantitative FRET imaging of leptin receptor oligomerization kinetics in single cells. Biol. Cell 97 905–919. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

