Study of an RNA helicase implicates small RNA-noncoding RNA interactions in programmed DNA elimination in Tetrahymena
- PMID: 18708581
- PMCID: PMC2518816
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.481908
Study of an RNA helicase implicates small RNA-noncoding RNA interactions in programmed DNA elimination in Tetrahymena
Abstract
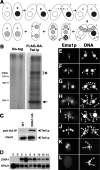
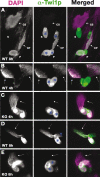
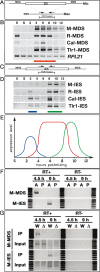
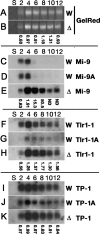
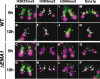
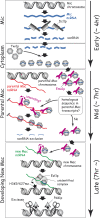
Tetrahymena eliminates micronuclear-limited sequences from the developing macronucleus during sexual reproduction. Homology between the sequences to be eliminated and approximately 28-nucleotide small RNAs (scnRNAs) associated with an Argonaute family protein Twi1p likely underlies this elimination process. However, the mechanism by which Twi1p-scnRNA complexes identify micronuclear-limited sequences is not well understood. We show that a Twi1p-associated putative RNA helicase Ema1p is required for the interaction between Twi1p and chromatin. This requirement explains the phenotypes of EMA1 KO strains, including loss of selective down-regulation of scnRNAs homologous to macronuclear-destined sequences, loss of H3K9 and K27 methylation in the developing new macronucleus, and failure to eliminate DNA. We further demonstrate that Twi1p interacts with noncoding transcripts derived from parental and developing macronuclei and this interaction is greatly reduced in the absence of Ema1p. We propose that Ema1p functions in DNA elimination by stimulating base-pairing interactions between scnRNAs and noncoding transcripts in both parental and developing new macronuclei.
Figures


References
-
- Bühler M., Verdel A., Moazed D. Tethering RITS to a nascent transcript initiates RNAi- and heterochromatin-dependent gene silencing. Cell. 2006;125:873–886. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
