The volatile anesthetic isoflurane perturbs conformational activation of integrin LFA-1 by binding to the allosteric regulatory cavity
- PMID: 18708587
- PMCID: PMC2614612
- DOI: 10.1096/fj.08-113324
The volatile anesthetic isoflurane perturbs conformational activation of integrin LFA-1 by binding to the allosteric regulatory cavity
Abstract
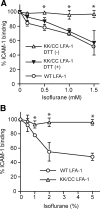
The molecular and structural basis of anesthetic interactions with conformations and functionalities of cell surface receptors remains to be elucidated. We have demonstrated that the widely used volatile anesthetic isoflurane blocks the activation-dependent conformational conversion of integrin lymphocyte function associated antigen-1 (LFA-1), the major leukocyte cell adhesion molecule, to a high-affinity configuration. Perturbation of LFA-1 activation by isoflurane at clinically relevant concentrations leads to the inhibition of T-cell interactions with target cells as well as ligand-triggered intracellular signaling. Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy reveals that isoflurane binds within a cavity in the LFA-1 ligand-binding domain, which is a previously identified drug-binding site for allosteric small-molecule antagonists that stabilize LFA-1 in a low-affinity conformation. These results provide a potential mechanism for the immunomodulatory properties of isoflurane.
Figures



References
-
- McBride W T, Armstrong M A, McBride S J. Immunomodulation: an important concept in modern anaesthesia. Anaesthesia. 1996;51:465–473. - PubMed
-
- Heindl B, Reichle F M, Zahler S, Conzen P F, Becker B F. Sevoflurane and isoflurane protect the reperfused guinea pig heart by reducing postischemic adhesion of polymorphonuclear neutrophils. Anesthesiology. 1999;91:521–530. - PubMed
-
- Mobert J, Zahler S, Becker B F, Conzen P F. Inhibition of neutrophil activation by volatile anesthetics decreases adhesion to cultured human endothelial cells. Anesthesiology. 1999;90:1372–1381. - PubMed
-
- Hayes J K, Havaleshko D M, Plachinta R V, Rich G F. Isoflurane pretreatment supports hemodynamics and leukocyte rolling velocities in rat mesentery during lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammation. Anesth Analg. 2004;98:999–1006. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

