Role of P63 (CKAP4) in binding of surfactant protein-A to type II pneumocytes
- PMID: 18708633
- PMCID: PMC2575944
- DOI: 10.1152/ajplung.90233.2008
Role of P63 (CKAP4) in binding of surfactant protein-A to type II pneumocytes
Abstract
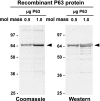
We have recently described a putative receptor for lung surfactant protein-A (SP-A) on rat type II pneumocytes. The receptor, P63, is a 63-kDa type II transmembrane protein. Coincubation of type II cells with P63 antibody (Ab) reversed the inhibitory effect of SP-A on secretagogue-stimulated surfactant secretion from type II cells. To further characterize SP-A interactions with P63, we expressed recombinant P63 protein in Escherichia coli and generated antibodies to P63. Immunogold electron microscopy confirmed endoplasmic reticulum and plasma membrane localization of P63 in type II cells with prominent labeling of microvilli. Binding characteristics of iodinated SP-A to type II cells in the presence of P63 Ab were determined. Binding (4 degrees C, 1 h) of (125)I-SP-A to type II cells demonstrated both specific (calcium-dependent) and nonspecific (calcium-independent) components. Ab to P63 protein blocked the specific binding of (125)I-SP-A to type II cells and did not change the nonspecific SP-A association. A549 cells, a pneumocyte model cell line, expressed substantial levels of P63 and demonstrated specific binding of (125)I-SP-A that was inhibited by the P63 Ab. The secretagogue (cAMP)-stimulated increase in calcium-dependent binding of SP-A to type II cells was blocked by the presence of P63 Ab. Transfection of type II cells with small interfering RNA to P63 reduced P63 protein expression, attenuated P63-specific SP-A binding, and reversed the ability of SP-A to prevent surfactant secretion from the cells. Our results further substantiate the role of P63 as an SP-A receptor protein localized on the surface of lung type II cells.
Figures










References
-
- Bates SR, Dodia C, Fisher AB. Surfactant protein A regulates uptake of pulmonary surfactant by lung type II cells on microporous membranes. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 267: L753–L760, 1994. - PubMed
-
- Bates SR, Dodia C, Tao JQ, Fisher AB. Surfactant protein-A plays an important role in lung surfactant clearance: evidence using the surfactant protein-A gene-targeted mouse. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 294: L325–L333, 2008. - PubMed
-
- Bates SR, Tao JQ, Notarfrancesco K, DeBolt K, Shuman H, Fisher AB. Effect of surfactant protein A on granular pneumocyte surfactant secretion in vitro. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 285: L1055–L1065, 2003. - PubMed
-
- Bligh EG, Dyer WJ. A rapid method of total lipid extraction and purification. Can J Med Sci 37: 911–917, 1959. - PubMed
-
- Bradford M A rapid and sensitive method for quantitation of microgram quantities of proteins utilizing the principle of protein dye binding. Anal Biochem 72: 248–254, 1976. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

