Prospects and challenges in using patient-reported outcomes in clinical practice
- PMID: 18709564
- PMCID: PMC3119524
- DOI: 10.1007/s11136-008-9379-5
Prospects and challenges in using patient-reported outcomes in clinical practice
Abstract
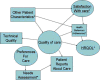
Background: Patient-reported measures include preferences and reports about care received, health behaviors, and outcomes of care (patient satisfaction and health-related quality of life). These measures are a core aspect of health care, but there is much to be learned about how to use them to improve clinical practice.
Method: We specify linkages among different patient-reported measures and focus upon the prospects and challenges for use of patient-reported outcomes in clinical practice.
Results: Patient-reported measures are important throughout the continuum of patient care. At the initial visit, patient-reported outcomes provide information about what is important to the patient, the patient's current behaviors, and the patient's baseline health-related quality of life. At subsequent visits, patient-reported outcomes help evaluate disease progression or regression as well as treatment effects.
Conclusions: Patient-reported measures can help clinicians target interventions that will improve patient outcomes of care. However, there are a number of challenges in using patient-reported outcomes in clinical practice.
Similar articles
-
The future of Cochrane Neonatal.Early Hum Dev. 2020 Nov;150:105191. doi: 10.1016/j.earlhumdev.2020.105191. Epub 2020 Sep 12. Early Hum Dev. 2020. PMID: 33036834
-
Virtualized clinical studies to assess the natural history and impact of gut microbiome modulation in non-hospitalized patients with mild to moderate COVID-19 a randomized, open-label, prospective study with a parallel group study evaluating the physiologic effects of KB109 on gut microbiota structure and function: a structured summary of a study protocol for a randomized controlled study.Trials. 2021 Apr 2;22(1):245. doi: 10.1186/s13063-021-05157-0. Trials. 2021. PMID: 33810796 Free PMC article.
-
Patient-reported outcome measures for monitoring primary care patients with depression: the PROMDEP cluster RCT and economic evaluation.Health Technol Assess. 2024 Mar;28(17):1-95. doi: 10.3310/PLRQ4216. Health Technol Assess. 2024. PMID: 38551155 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Patient-reported outcome measures: the importance of patient satisfaction in surgery.Surgery. 2009 Sep;146(3):435-43. doi: 10.1016/j.surg.2009.03.019. Epub 2009 May 28. Surgery. 2009. PMID: 19715800 Review.
-
Folic acid supplementation and malaria susceptibility and severity among people taking antifolate antimalarial drugs in endemic areas.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Feb 1;2(2022):CD014217. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD014217. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 36321557 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Preoperative psychometric properties of visual analog scale asessments for function, pain, and strength compared with legacy upper extremity outcome measures in glenohumeral osteoarthritis.JSES Int. 2020 Jun 17;4(3):443-448. doi: 10.1016/j.jseint.2020.03.006. eCollection 2020 Sep. JSES Int. 2020. PMID: 32939466 Free PMC article.
-
Psychometric properties of visual analog scale assessments for function, pain, and strength compared with disease-specific upper extremity outcome measures in rotator cuff repair.JSES Int. 2020 May 23;4(3):619-624. doi: 10.1016/j.jseint.2020.04.012. eCollection 2020 Sep. JSES Int. 2020. PMID: 32939496 Free PMC article.
-
Patient experiences with patient-reported outcome measures: an interview study of patients undergoing total hip- and knee arthroplasty.J Patient Rep Outcomes. 2023 Mar 2;7(1):19. doi: 10.1186/s41687-023-00561-3. J Patient Rep Outcomes. 2023. PMID: 36862315 Free PMC article.
-
Health perceptions and symptom burden in primary care: measuring health using audio computer-assisted self-interviews.Qual Life Res. 2015 Jul;24(7):1575-83. doi: 10.1007/s11136-014-0884-4. Epub 2014 Dec 7. Qual Life Res. 2015. PMID: 25488793
-
Patient-Reported Outcomes Measurement Information System as a Clinical Tool for Capturing the Patient Perspective in Pediatric Inflammatory Bowel Disease: A Narrative Review.Children (Basel). 2024 Dec 6;11(12):1492. doi: 10.3390/children11121492. Children (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39767921 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- The Healthcare Effectiveness Data and Information Set (HEDIS) [Accessed 17 March 2008];National Committee for Quality Assurance. 2008 Available from: http://www.ncqa.org/tabid/59/Default.aspx.
-
- Department of Veterans Affairs [Accessed 17 March 2008];External Peer Review Program. VHA Directive 2001-015. 2001 Available from: http://www1.va.gov/VHAPUBLICATIONS/ViewPublication.asp?pub_ID=103.
-
- Food and Drug Administration [Accessed 17 March 2008];Guidance for industry. Patient-reported outcome measures: Use in medical product development to support labeling claims. 2006 Available from: http:// www.fda.gov/OHRMS/DOCKETS/98fr/06d-0044-gdl0001.pdf. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Makoul G. Essential elements of communication in medical encounters: The Kalamazoo consensus statement. Academic Medicine. 2001;76(4):390–393. doi:10.1097/00001888-20010400000021. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical