Strong correlation between SHAPE chemistry and the generalized NMR order parameter (S2) in RNA
- PMID: 18710236
- PMCID: PMC2712629
- DOI: 10.1021/ja804541s
Strong correlation between SHAPE chemistry and the generalized NMR order parameter (S2) in RNA
Abstract
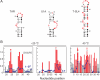
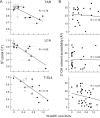
The functions of most RNA molecules are critically dependent on the distinct local dynamics that characterize secondary structure and tertiary interactions and on structural changes that occur upon binding by proteins and small molecule ligands. Measurements of RNA dynamics at nucleotide resolution set the foundation for understanding the roles of individual residues in folding, catalysis, and ligand recognition. In favorable cases, local order in small RNAs can be quantitatively analyzed by NMR in terms of a generalized order parameter, S2. Alternatively, SHAPE (selective 2'-hydroxyl acylation analyzed by primer extension) chemistry measures local nucleotide flexibility in RNAs of any size using structure-sensitive reagents that acylate the 2'-hydroxyl position. In this work, we compare per-residue RNA dynamics, analyzed by both S2 and SHAPE, for three RNAs: the HIV-1 TAR element, the U1A protein binding site, and the Tetrahymena telomerase stem loop 4. We find a very strong correlation between the two measurements: nucleotides with high SHAPE reactivities consistently have low S2 values. We conclude that SHAPE chemistry quantitatively reports local nucleotide dynamics and can be used with confidence to analyze dynamics in large RNAs, RNA-protein complexes, and RNAs in vivo.
Figures
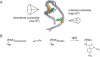
References
-
- Korostelev A, Noller HF. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2007;32:434–441. - PubMed
- Buchmueller KL, Webb AE, Richardson DA, Weeks KM. Nature Struct. Biol. 2000;7:362–366. - PubMed
- Maity TS, Weeks KM. J. Mol. Biol. 2007;369:512–524. - PMC - PubMed
- Bokinsky G, Nivón LG, Liu S, Chai G, Hong M, Weeks KM, Zhuang X. J. Mol. Biol. 2006;361:771–784. - PMC - PubMed
- Kim JN, Breaker RR. Biol. Cell. 2008;100:1–11. - PubMed
-
- Guéron M, Leroy JL. Methods Enzymol. 1995;261:383–413. - PubMed
-
- Lipari G, Szabo A. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1982;104:4546–4559.
- Lipari G, Szabo A. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1982;104:4559–4570.
-
- Dayie KT, Brodsky AS, Williamson JR. J. Mol. Biol. 2002;317:263–278. - PubMed
- Vallurupalli P, Scott L, Hennig M, Williamson JR, Kay LE. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006;128:9346–9347. - PubMed
- Hansen AL, Al-Hashimi HM. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2007;129:16072–16082. - PubMed
- Blad H, Reiter NJ, Abildgaard F, Markley JL, Butcher SE. J. Mol. Biol. 2005;353:540–555. - PubMed
- Hoogstraten CG, Wank JR, Pardi A. Biochemistry. 2000;39:9951–9958. - PubMed
- Hall KB, Tang C. Biochemistry. 1998;37:9323–9332. - PubMed
- D'Souza V, Dey A, Habib D, Summers MF. J. Mol. Biol. 2004;337:427–442. - PubMed
- Duchardt E, Schwalbe H. J. Biomol. NMR. 2005;32:295–308. - PubMed
- Ferner J, Villa A, Duchardt E, Widjajakusuma E, Wöhnert J, Stock G, Schwalbe H. Nucl. Acids Res. 2008;36:1928–1940. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

