Mechanistic and structural analysis of aminoglycoside N-acetyltransferase AAC(6')-Ib and its bifunctional, fluoroquinolone-active AAC(6')-Ib-cr variant
- PMID: 18710261
- PMCID: PMC2855648
- DOI: 10.1021/bi800664x
Mechanistic and structural analysis of aminoglycoside N-acetyltransferase AAC(6')-Ib and its bifunctional, fluoroquinolone-active AAC(6')-Ib-cr variant
Abstract
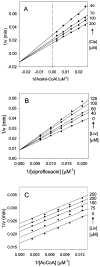
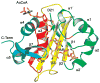
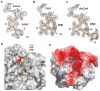
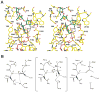
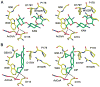
Enzymatic modification of aminoglycoside antibiotics mediated by regioselective aminoglycoside N-acetyltransferases is the predominant cause of bacterial resistance to aminoglycosides. A recently discovered bifunctional aminoglycoside acetyltransferase (AAC(6')-Ib variant, AAC(6')-Ib-cr) has been shown to catalyze the acetylation of fluoroquinolones as well as aminoglycosides. We have expressed and purified AAC(6')-Ib-wt and its bifunctional variant AAC(6')-Ib-cr in Escherichia coli and characterized their kinetic and chemical mechanism. Initial velocity and dead-end inhibition studies support an ordered sequential mechanism for the enzyme(s). The three-dimensional structure of AAC(6')-Ib-wt was determined in various complexes with donor and acceptor ligands to resolutions greater than 2.2 A. Observation of the direct, and optimally positioned, interaction between the 6'-NH 2 and Asp115 suggests that Asp115 acts as a general base to accept a proton in the reaction. The structure of AAC(6')-Ib-wt permits the construction of a molecular model of the interactions of fluoroquinolones with the AAC(6')-Ib-cr variant. The model suggests that a major contribution to the fluoroquinolone acetylation activity comes from the Asp179Tyr mutation, where Tyr179 makes pi-stacking interactions with the quinolone ring facilitating quinolone binding. The model also suggests that fluoroquinolones and aminoglycosides have different binding modes. On the basis of kinetic properties, the pH dependence of the kinetic parameters, and structural information, we propose an acid/base-assisted reaction catalyzed by AAC(6')-Ib-wt and the AAC(6')-Ib-cr variant involving a ternary complex.
Figures

References
-
- Magnet S, Blanchard JS. Molecular insights into aminoglycoside action and resistance. Chem Rev. 2005;105:477–498. - PubMed
-
- Miller GH, Sabatelli FJ, Naples L, Hare RS, Shaw KJ. The changing nature of aminoglycoside resistance mechanisms and the role of isepamicin—a new broad-spectrum aminoglycoside. The Aminoglycoside Resistance Study Groups. J Chemother. 1995;7(Suppl 2):31–44. - PubMed
-
- Wright GD. Aminoglycoside-modifying enzymes. Curr Opin Microbiol. 1999;2:499–503. - PubMed
-
- Davies J, Wright GD. Bacterial resistance to aminoglycoside antibiotics. Trends Microbiol. 1997;5:234–240. - PubMed
-
- Poole K. Efflux-mediated antimicrobial resistance. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2005;56:20–51. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

