Human lactoferrin induces apoptosis-like cell death in Candida albicans: critical role of K+-channel-mediated K+ efflux
- PMID: 18710913
- PMCID: PMC2573133
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.01597-07
Human lactoferrin induces apoptosis-like cell death in Candida albicans: critical role of K+-channel-mediated K+ efflux
Abstract
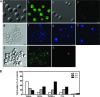
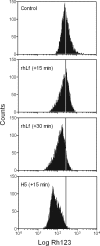
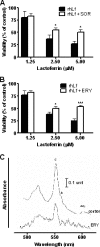
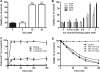
Human lactoferrin (hLf) induced an apoptosis-like phenotype in Candida albicans cells, which includes phosphatidylserine externalization, nuclear chromatin condensation, DNA degradation, and increased reactive oxygen species (ROS) production. Intracellular ROS accumulation was seen to correlate with candidacidal activity in hLf-treated cells. Mitochondrial activity was involved as indicated by mitochondrial depolarization and increased hLf resistance of cells preincubated with sordarin or erythromycin, the latter of which inhibits protein synthesis in mitoribosomes. Interestingly, Cl(-)- and K(+)-channel blockers prevented the hLf antimicrobial activity, but only when cells were pretreated with the blocking agent (tetraethylammonium) prior to the hLf-induced K(+)-release period. These results indicate for the first time that K(+)-channel-mediated K(+) efflux is required for the progression of apoptosis-like process in yeast, suggesting that this essential apoptotic event of higher eukaryotes has been evolutionary conserved among species ranging from yeasts to humans.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Cytosolic Acidification Is the First Transduction Signal of Lactoferrin-induced Regulated Cell Death Pathway.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Nov 20;20(23):5838. doi: 10.3390/ijms20235838. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31757076 Free PMC article.
-
Internal thiols and reactive oxygen species in candidacidal activity exerted by an N-terminal peptide of human lactoferrin.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2002 Jun;46(6):1634-9. doi: 10.1128/AAC.46.6.1634-1639.2002. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2002. PMID: 12019068 Free PMC article.
-
Antifungal Mechanism of Action of Lactoferrin: Identification of H+-ATPase (P3A-Type) as a New Apoptotic-Cell Membrane Receptor.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2016 Jun 20;60(7):4206-16. doi: 10.1128/AAC.03130-15. Print 2016 Jul. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2016. PMID: 27139463 Free PMC article.
-
Role of potassium channels in chlorogenic acid-induced apoptotic volume decrease and cell cycle arrest in Candida albicans.Biochim Biophys Acta Gen Subj. 2017 Mar;1861(3):585-592. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagen.2016.12.026. Epub 2016 Dec 28. Biochim Biophys Acta Gen Subj. 2017. PMID: 28040564
-
Reactive oxygen species modulate itraconazole-induced apoptosis via mitochondrial disruption in Candida albicans.Free Radic Res. 2018 Jan;52(1):39-50. doi: 10.1080/10715762.2017.1407412. Epub 2017 Dec 4. Free Radic Res. 2018. PMID: 29157011 Review.
Cited by
-
Live-cell imaging and analysis shed light on the complexity and dynamics of antimicrobial Peptide action.Front Immunol. 2012 Aug 14;3:248. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2012.00248. eCollection 2012. Front Immunol. 2012. PMID: 22912634 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Whole-Genome Approach to Understanding the Mechanism of Action of a Histatin 5-Derived Peptide.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2020 Feb 21;64(3):e01698-19. doi: 10.1128/AAC.01698-19. Print 2020 Feb 21. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2020. PMID: 31843998 Free PMC article.
-
Redox modulation of the fetal cardiovascular defence to hypoxaemia.J Physiol. 2010 Nov 1;588(Pt 21):4235-47. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2010.196402. J Physiol. 2010. PMID: 20807788 Free PMC article.
-
The Antimicrobial Activity of Human Defensins at Physiological Non-Permeabilizing Concentrations Is Caused by the Inhibition of the Plasma Membrane H+-ATPases.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jul 4;25(13):7335. doi: 10.3390/ijms25137335. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39000442 Free PMC article.
-
Thriving within the host: Candida spp. interactions with phagocytic cells.Med Microbiol Immunol. 2013 Jun;202(3):183-95. doi: 10.1007/s00430-013-0288-z. Epub 2013 Jan 25. Med Microbiol Immunol. 2013. PMID: 23354731 Review.
References
-
- Baev, D., A. Rivetta, S. Vylkova, J. N. Sun, G. F. Zeng, C. L. Slayman, and M. Edgerton. 2004. The TRK1 potassium transporter is the critical effector for killing of Candida albicans by the cationic protein, Histatin 5. J. Biol. Chem. 279:55060-55072. - PubMed
-
- Balzan, R., K. Sapienza, D. R. Galea, N. Vassallo, H. Frey, and W. H. Bannister. 2004. Aspirin commits yeast cells to apoptosis depending on carbon source. Microbiology 150:109-115. - PubMed
-
- Bortner, C. D., and J. A. Cidlowski. 2002. Apoptotic volume decrease and the incredible shrinking cell. Cell Death Differ. 9:1307-1310. - PubMed
-
- Bradford, M. 1976. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal. Biochem. 72:248-254. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

