Engineered recombinant human paraoxonase 1 (rHuPON1) purified from Escherichia coli protects against organophosphate poisoning
- PMID: 18711144
- PMCID: PMC2529096
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0805865105
Engineered recombinant human paraoxonase 1 (rHuPON1) purified from Escherichia coli protects against organophosphate poisoning
Abstract
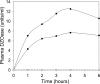
The high-density lipoprotein-associated enzyme paraoxonase 1 (PON1) hydrolyzes lactones, aromatic esters, and neurotoxic organophosphorus (OP) compounds, including insecticide metabolites and nerve agents. Experiments with mice lacking PON1 (PON1(-/-) mice) have established that plasma PON1 protects against chlorpyrifos/chlorpyrifos-oxon and diazinon/diazoxon (DZO) exposure but does not protect against parathion/paraoxon or nerve agents. The catalytic efficiency of PON1 determines whether or not it will protect against a given OP exposure. Expression of active recombinant human PON1 (rHuPON1) in Escherichia coli provides a system in which PON1 can be engineered to achieve a catalytic efficiency sufficient to protect against or treat specific OP exposures. Here, we describe the generation of highly purified engineered rHuPON1(K192) that protects against DZO exposure when injected into PON1(-/-) mice. The injected rHuPON1 is nontoxic, persists in serum for at least 2 days after injection, and provides protection against DZO exposures of at least three times the median lethal dose value.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Comment in
-
PON1 multitasks to protect health.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008 Sep 2;105(35):12639-40. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0807062105. Epub 2008 Aug 27. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008. PMID: 18753632 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- World Health Organization. Informal Consultation on Planning Strategy for the Prevention of Pesticide Poisoning. Geneva: WHO; 1986. WHO/VBC/86.926.
-
- World Health Organization. Public Health Impact of Pesticides Used in Agriculture. Geneva: WHO; 1990.
-
- Johnson MK. The target for initiation of delayed neurotoxicity by organophosphorus esters: Biochemical studies and toxicological applications. Rev Biochem Toxicol. 1982;4:141–212.
-
- Shih TM, McDonough JH. Organophosphorus nerve agent-induced seizures and efficacy of atropine sulfate as anticonvulsant treatment: Pharmacologic mechanisms. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 1999;64:147–153. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

