Structural and dynamic interfacial properties of the lipoprotein initiating domain of apolipoprotein B
- PMID: 18711207
- PMCID: PMC2602867
- DOI: 10.1194/jlr.M800324-JLR200
Structural and dynamic interfacial properties of the lipoprotein initiating domain of apolipoprotein B
Abstract
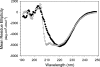
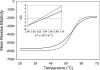
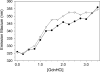
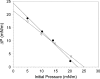
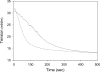
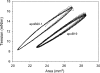
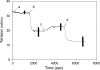
To better understand the earliest steps in the assembly of triglyceride (TG)-rich lipoproteins, we compared the biophysical and interfacial properties of two closely related apolipoprotein B (apoB) truncation mutants, one of which contains the complete lipoprotein initiating domain (apoB20.1; residues 1-912), and one of which, by virtue of a 50 amino acid C-terminal truncation, is incapable of forming nascent lipoproteins (apoB19; residues 1-862). Spectroscopic studies detected no major differences in secondary structure, and only minor differences in conformation and thermodynamic stability, between the two truncation mutants. Monolayer studies revealed that both apoB19 and apoB20.1 bound to and penetrated egg phosphatidylcholine (EPC) monolayers; however, the interfacial exclusion pressure of apoB20.1 was higher than apoB19 (25.1 mN/m vs. 22.8 mN/m). Oil drop tensiometry revealed that both proteins bound rapidly to the hydrophobic triolein/water interface, reducing interfacial tension by approximately 20 mN/m. However, when triolein drops were first coated with phospholipids (PL), apoB20.1 bound with faster kinetics than apoB19 and also displayed greater interfacial elasticity (26.9 +/- 0.8 mN/m vs. 22.9 +/- 0.8 mN/m). These data establish that the transition of apoB to assembly competence is accompanied by increases in surface activity and elasticity, but not by significant changes in global structure.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Self-association and lipid binding properties of the lipoprotein initiating domain of apolipoprotein B.J Biol Chem. 2006 Mar 31;281(13):8871-6. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M507657200. Epub 2006 Jan 3. J Biol Chem. 2006. PMID: 16407215
-
Interfacial properties of amphipathic beta strand consensus peptides of apolipoprotein B at oil/water interfaces.J Lipid Res. 2004 Sep;45(9):1704-15. doi: 10.1194/jlr.M400106-JLR200. Epub 2004 Jul 1. J Lipid Res. 2004. PMID: 15231853
-
Surface study of apoB1694-1880, a sequence that can anchor apoB to lipoproteins and make it nonexchangeable.J Lipid Res. 2009 Jul;50(7):1340-52. doi: 10.1194/jlr.M900040-JLR200. Epub 2009 Feb 26. J Lipid Res. 2009. PMID: 19251580 Free PMC article.
-
Electronegative low-density lipoprotein. A link between apolipoprotein B misfolding, lipoprotein aggregation and proteoglycan binding.Curr Opin Lipidol. 2012 Oct;23(5):479-86. doi: 10.1097/MOL.0b013e328357c933. Curr Opin Lipidol. 2012. PMID: 22964994 Review.
-
Progress towards understanding the role of microsomal triglyceride transfer protein in apolipoprotein-B lipoprotein assembly.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2000 Jun 26;1486(1):72-83. doi: 10.1016/s1388-1981(00)00049-4. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2000. PMID: 10856714 Review.
Cited by
-
Impact of murine intestinal apolipoprotein A-IV expression on regional lipid absorption, gene expression, and growth.J Lipid Res. 2011 Nov;52(11):1984-94. doi: 10.1194/jlr.M017418. Epub 2011 Aug 12. J Lipid Res. 2011. PMID: 21840868 Free PMC article.
-
Interfacial properties of apolipoprotein B292-593 (B6.4-13) and B611-782 (B13-17). Insights into the structure of the lipovitellin homology region in apolipoprotein B.Biochemistry. 2010 May 11;49(18):3898-907. doi: 10.1021/bi100056v. Biochemistry. 2010. PMID: 20353182 Free PMC article.
-
Surface tensiometry of apolipoprotein B domains at lipid interfaces suggests a new model for the initial steps in triglyceride-rich lipoprotein assembly.J Biol Chem. 2014 Mar 28;289(13):9000-12. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.540955. Epub 2014 Feb 10. J Biol Chem. 2014. PMID: 24515109 Free PMC article.
-
Apolipoprotein C-I binds more strongly to phospholipid/triolein/water than triolein/water interfaces: a possible model for inhibiting cholesterol ester transfer protein activity and triacylglycerol-rich lipoprotein uptake.Biochemistry. 2012 Feb 14;51(6):1238-48. doi: 10.1021/bi2015212. Epub 2012 Feb 2. Biochemistry. 2012. PMID: 22264166 Free PMC article.
-
Interfacial properties of high-density lipoprotein-like lipid droplets with different lipid and apolipoprotein A-I compositions.Biophys J. 2013 May 21;104(10):2193-201. doi: 10.1016/j.bpj.2013.02.058. Biophys J. 2013. PMID: 23708359 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Davidson N. O., and G. S. Shelness. 2000. Apolipoprotein B: mRNA editing, lipoprotein assembly, and presecretory degradation. Annu. Rev. Nutr. 20 169–193. - PubMed
-
- Fisher E. A., and H. N. Ginsberg. 2002. Complexity in the secretory pathway: the assembly and secretion of apolipoprotein B-containing lipoproteins. J. Biol. Chem. 277 17377–17380. - PubMed
-
- Hussain M. M., S. Fatma, X. Y. Pan, and J. Iqbal. 2005. Intestinal lipoprotein assembly. Curr. Opin. Lipidol. 16 281–285. - PubMed
-
- Shelness G. S., and A. S. Ledford. 2005. Evolution and mechanism of apolipoprotein B-containing lipoprotein assembly. Curr. Opin. Lipidol. 16 325–332. - PubMed
-
- Davis R. A., and T. Y. Hui. 2001. 2000 George Lyman Duff memorial lecture—atherosclerosis is a liver disease of the heart. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 21 887–898. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

