Muscle wasting and interleukin-6-induced atrogin-I expression in the cachectic Apc ( Min/+ ) mouse
- PMID: 18712412
- PMCID: PMC2867110
- DOI: 10.1007/s00424-008-0574-6
Muscle wasting and interleukin-6-induced atrogin-I expression in the cachectic Apc ( Min/+ ) mouse
Abstract
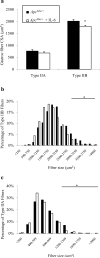
Interleukin-6 (IL-6) is necessary for cachexia in Apc ( Min/+ ) mice, but the mechanisms inducing this myofiber wasting have not been established. The purpose of this study was to examine gastrocnemius muscle wasting in the Apc ( Min/+ ) mouse and to determine IL-6 regulated mechanisms contributing to muscle loss. Gastrocnemius type IIB mean fiber cross-sectional area (CSA) from Apc ( Min/+ ) mice decreased 32% between 13 and 22 weeks of age. Apc ( Min/+ ) mice lacking IL-6 did not have type IIB fiber atrophy, while overexpression of circulating IL-6 exacerbated the loss of type IIB fiber CSA in Apc ( Min/+ ) mice. Muscle Atrogin-I mRNA expression was induced at least ninefold at 18 and 22 weeks of age compared to 13-week-old mice. Atrogin-I gene expression was also induced by overexpression of circulating IL-6. These data suggest that high circulating IL-6 levels induce type IIB fiber CSA loss in Apc ( Min/+ ) mice, and circulating IL-6 is sufficient to regulate Atrogin-I gene expression in cachectic mice.
Figures




References
-
- Price SA, Tisdale MJ. Mechanism of inhibition of a tumor lipid-mobilizing factor by eicosapentaenoic acid. Cancer Res. 1998;58:4827–4831. - PubMed
-
- Giordano A, Calvani M, Petillo O, Carteni M, Melone MR, Peluso G. Skeletal muscle metabolism in physiology and in cancer disease. J Cell Biochem. 2003;90:170–186. - PubMed
-
- al-Majid S, McCarthy DO. Resistance exercise training attenuates wasting of the extensor digitorum longus muscle in mice bearing the colon-26 adenocarcinoma. Biol Res Nurs. 2001;2:155–166. - PubMed
-
- Ardies CM. Exercise, cachexia, and cancer therapy: a molecular rationale. Nutr Cancer. 2002;42:143–157. - PubMed
-
- Khalfoun B, Thibault F, Watier H, Bardos P, Lebranchu Y. Docosahexaenoic and eicosapentaenoic acids inhibit in vitro human endothelial cell production of interleukin-6. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1997;400B:589–597. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

