B cell depletion with anti-CD79 mAbs ameliorates autoimmune disease in MRL/lpr mice
- PMID: 18713966
- PMCID: PMC2865432
- DOI: 10.4049/jimmunol.181.5.2961
B cell depletion with anti-CD79 mAbs ameliorates autoimmune disease in MRL/lpr mice
Abstract
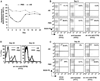
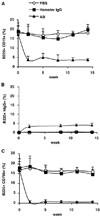
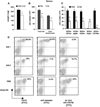
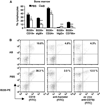
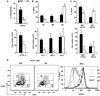
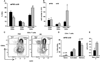
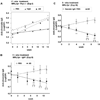
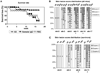
MRL/lpr mice develop a spontaneous systemic lupus erythematosus-like autoimmune syndrome due to a dysfunctional Fas receptor, with contributions from other less well-defined genetic loci. The removal of B cells by genetic manipulation not only prevents autoantibody formation, but it also results in substantially reduced T cell activation and kidney inflammation. To determine whether B cell depletion by administration of Abs is effective in lupus mice with an intact immune system and established disease, we screened several B cell-specific mAbs and found that a combination of anti-CD79alpha and anti-CD79beta Abs was most effective at depleting B cells in vivo. Anti-CD79 therapy started at 4-5 mo of age in MRL/lpr mice significantly decreased B cells (B220(+)CD19(+)) in peripheral blood, bone marrow, and spleens. Treated mice also had a significant increase in the number of both double-negative T cells and naive CD4(+) T cells, and a decreased relative abundance of CD4(+) memory cells. Serum anti-chromatin IgG levels were significantly decreased compared with controls, whereas serum anti-dsDNA IgG, total IgG, or total IgM were unaffected. Overall, survival was improved with lower mean skin scores and significantly fewer focal inflammatory infiltrates in submandibular salivary glands and kidneys. Anti-CD79 mAbs show promise as a potential treatment for systemic lupus erythematosus and as a model for B cell depletion in vivo.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no financial conflicts of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Rivera A, Chen CC, Ron N, Dougherty JP, Ron Y. Role of B cells as antigen-presenting cells in vivo revisited: antigen-specific B cells are essential for T cell expansion in lymph nodes and for systemic T cell responses to low antigen concentrations. Int. Immunol. 2001;13:1583–1593. - PubMed
-
- Lipsky PE. Systemic lupus erythematosus: an autoimmune disease of B cell hyperactivity. Nat. Immunol. 2001;2:764–766. - PubMed
-
- Youinou P, Jamin C, Pers JO, Berthou C, Saraux A, Renaudineau Y. B lymphocytes are required for development and treatment of autoimmune diseases. Ann. NY Acad. Sci. 2005;1050:19–33. - PubMed
-
- Lund FE, Garvy BA, Randall TD, Harris DP. Regulatory roles for cytokine-producing B cells in infection and autoimmune disease. Curr. Dir. Autoimmun. 2005;8:25–54. - PubMed
-
- Chan OT, Shlomchik MJ. Cutting edge: B cells promote CD8+ T cell activation in MRL-Faslpr mice independently of MHC class I antigen presentation. J. Immunol. 2000;164:1658–1662. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

