Comparison of two treatment approaches for prostate cancer: intensity-modulated radiation therapy combined with 125I seed-implant brachytherapy or 125I seed-implant brachytherapy alone
- PMID: 18714275
- PMCID: PMC5721712
- DOI: 10.1120/jacmp.v9i2.2283
Comparison of two treatment approaches for prostate cancer: intensity-modulated radiation therapy combined with 125I seed-implant brachytherapy or 125I seed-implant brachytherapy alone
Abstract
The purpose of the present study was to assess the results of two different treatment approaches for clinically localized prostate cancer: intensity-modulated radiation therapy (IMRT) followed by 125I seed-implant brachytherapy and 125I seed-implant brachytherapy alone. We studied our 30 most recent consecutive patients. The sample population consisted of 15 cases treated with IMRT (50.4 Gy) followed by 125I seed-implant boost (95 Gy), and 15 cases treated with 125I seed implant only (144 Gy). We analyzed established dosimetric indices and various clinical parameters. In addition, we also evaluated and compared the acute urinary morbidities of the two treatment approaches, as assessed by the international prostate symptom score (IPSS). In our series, acute urinary morbidity was slightly increased with IMRT followed by 125I seed-implant brachytherapy as compared with 125I seed-implant brachytherapy alone. In addition, we observed no statistically significant correlation between the IPSS and the maximum or mean urethral dose. The combination of IMRT and seed-implant brachytherapy presents an alternative opportunity to treat clinically localized prostate cancer. The full potential of the procedure needs to be further investigated.
Figures
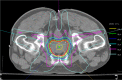
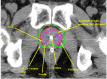
Similar articles
-
Intensity-modulated radiotherapy causes fewer side effects than three-dimensional conformal radiotherapy when used in combination with brachytherapy for the treatment of prostate cancer.Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2012 Jun 1;83(2):630-5. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2011.06.2013. Epub 2011 Nov 16. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2012. PMID: 22099032
-
Combined brachytherapy with external beam radiotherapy for localized prostate cancer: reduced morbidity with an intraoperative brachytherapy planning technique and supplemental intensity-modulated radiation therapy.Brachytherapy. 2008 Jan-Mar;7(1):1-6. doi: 10.1016/j.brachy.2007.12.002. Brachytherapy. 2008. PMID: 18299108
-
Quality of life in patients who underwent 125I brachytherapy, 125I brachytherapy combined with three-dimensional conformal radiation therapy, or intensity-modulated radiation therapy, for prostate cancer.J Radiat Res. 2019 Mar 1;60(2):270-280. doi: 10.1093/jrr/rry101. J Radiat Res. 2019. PMID: 30576565 Free PMC article.
-
American Brachytherapy Society (ABS) recommendations for transperineal permanent brachytherapy of prostate cancer.Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1999 Jul 1;44(4):789-99. doi: 10.1016/s0360-3016(99)00069-3. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1999. PMID: 10386635 Review.
-
[Brachytherapy for prostate carcinoma].Nihon Igaku Hoshasen Gakkai Zasshi. 2005 Apr;65(2):87-91. Nihon Igaku Hoshasen Gakkai Zasshi. 2005. PMID: 15920966 Review. Japanese.
Cited by
-
Success of 125I-Seed Treatment in Vulvar Squamous-Cell Carcinoma with Aplastic Anemia: A Case Report.Onco Targets Ther. 2020 Dec 7;13:12561-12566. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S283006. eCollection 2020. Onco Targets Ther. 2020. PMID: 33324074 Free PMC article.
-
MR-guided 125I seed implantation treatment for maxillofacial malignant tumor.J Appl Clin Med Phys. 2021 Jan;22(1):92-99. doi: 10.1002/acm2.13112. Epub 2020 Dec 9. J Appl Clin Med Phys. 2021. PMID: 33295143 Free PMC article.
-
125I seed implantation for lymph node metastasis from radioactive iodine-refractory differentiated thyroid carcinoma: a study on short-term efficacy and dosimetry.Front Oncol. 2024 Jun 26;14:1325987. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1325987. eCollection 2024. Front Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38988713 Free PMC article.
References
-
- United States, National Institutes of Health (NIH), National Cancer Institute (NCI) . Prostate cancer progress report: addressing the recommendations of the prostate cancer progress review group. Washington (DC): U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, NIH, NCI; 2004. 5 pp.
-
- Barbiere J, Hanley J, Song Y, Dhaman AP, Chan MF. Concise matrix analysis of point‐based prostate targeting for intensity modulated radiation therapy. Technol Cancer Res Treat. 2007; 6 (1): 1–10. - PubMed
-
- Leibel SA, Fuks Z, Zelefsky MJ, et al. Technological advances in external‐beam therapy for the treatment of localized prostate cancer. Semin Oncol. 2003; 30 (5): 596–615. - PubMed
-
- Eng TY, Thomas CR Jr, Herman TS. Primary radiation therapy for localized prostate cancer. Urol Oncol. 2002; 7 (6): 239–257. - PubMed
-
- Zelefsky MJ, Whitmore WF Jr. Long‐term results of retropubic permanent 125iodine implantation of the prostate for clinically localized prostatic cancer. J Urol. 1997; 158 (1): 23–29. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

